Photocatalytic Removal of Malachite Green and Brilliant Blue Dyes from its Aqueous Solution: A Case Study of Factorial Experimental Design
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v65i2.1356Keywords:
Malachite green dye, factorial experimental design, photocatalytic processAbstract
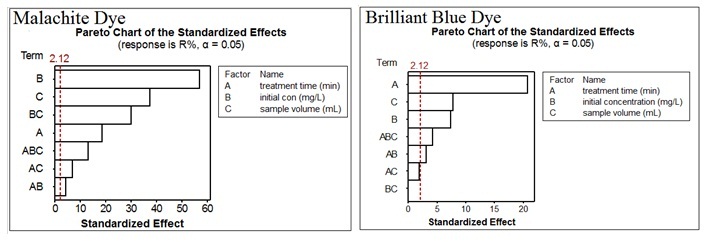
Abstract. In this present study, the investigation of the photocatalytic removal of malachite green and brilliant blue dyes from their aqueous solution using photocatalytic oxidation process was provided. The application of factorial experimental design for the analysis the results was the main objective in the present study. The photocatalytic removal of Malachite Green (MG) and Brilliant Blue (BB) dyes was carried out in aqueous solutions containing the dye and suspended of ZnO upon UV irradiation (high pressure mercury lamp Radium 125 W). The effect of different factors such as initial dye concentration, sample volume and treatment time was taken in account. All samples of MG and BB have been analysed at 617 and 620 nm, respectively. The linearity ranged between 5 and 50 mg/L for MG dye while it was ranged between 20 and 200 mg/L for BB dye. The linear regression, R2, was more than 0.995 for both dyes. The results revealed that factorial experimental design analysis has given a better indication to investigate the effects of factors. It was observed that the most of factors are significant for both dyes. Initial concentration and treatment time factors were the most significant factors for MG and BB dyes, respectively according to pareto chart.
Resumen. En este estudio se presenta una investigación sobre la remoción fotocatalítica de colorantes de verde de malaquita y azul brillante de soluciones acuosas mediante procesos de oxidación fotocatalítica. El objetivo principal de este trabajo fue la aplicación de un diseño experimental factorial para el análisis de los resultados. La remoción del verde de malaquita (MG) y azul brillante (BB) de soluciones acuosas se llevó a cabo mediante irradiación de luz UV en presencia de partículas de ZnO en suspensión. Para los experimentos, se usó una lámpara de mercurio a alta presión (Radium 125 W). Se consideraron los efectos de distintas variables, como la concentración inicial de cada colorante, el volumen de la muestra y el tiempo de tratamiento. Todas las muestras de MG y BB se analizaron a 617 y 620 nm, respectivamente. Se observó linealidad en los resultados en el intervalo de concentraciones entre 5 y 50 mg/L para el caso de MG, mientras que para el BB la linealidad se observó en el intervalo de concentraciones entre 20 y 200 mg/L. En ambos casos, los datos se ajustaron a modelos lineales con valores de R2 mayores a 0.995. Los resultados revelaron que el diseño experimental factorial permite investigar de mejor manera los efectos de diversos factores, encontrándose que la concentración inicial y el tiempo de tratamiento son los factores más importantes para la remoción de MG y BB, respectivamente, según se muestra en los gráficos de Pareto.
Downloads
References
Sartape, A. S.; Mandhare, A. M.; Jadhav, V. V.; Raut, P. D.; Anuse, M. A.; Kolekar, S. S. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3229?S3238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.12.019
Raducan, A.; Olteanu, A.; Puiu, M.; Oancea, D. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2008, 6, 89–92. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11532-007-0066-0
Visited on 01/06/2020 [http://www.culinarylore.com/ingredients:fdc-blue-no-1-brilliant-blue-fcf-food-dye]
Gao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Su, K.; Chen, R.; Peng, Y. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 215-225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.039
Sakamoto, M.; Ahmed, T.; Begum, S.; Huq, H. sustainability 2019, 11, 1951.https://doi.org/10.3390/su11071951
Aksu, Z.; Ertu?rul, S.; Dönmez, G. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 310-318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.02.027
Doan, H. D.; Weli, A.; Wu, J. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 151, 51-58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.01.041
Basha, C. A.; Bhadrinarayana, N. S.; Anantharaman, N.; Begum, K. M. S. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 71-78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.06.069
Solisio, C.; Panizza, M.; Paganelli, P.; Cerisola, G. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 1999, 26, 115-124. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-3449(98)00078-0
Sohrabi, M. R.; Ghavami, M. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 1235-1239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.09.114
Saien, J.; Soleymani, A. R. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 144, 506-512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.10.065
Faisal, M.; Tariq, M. A.; Muneer, M. Dyes Pigments 2007, 72, 233-239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2005.08.020
Chankhanittha, T.; Nanan, S. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2020, 582, 412-427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.08.061
González-Casamachin, D. A.; De la Rosa, J. R.; Lucio-Ortiz, C. J.; De Rio, D. A. D. H.; Martínez-Vargas, D. X.; Flores-Escamilla, G. A.; ... Moctezuma-Velazquez, E. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 373, 325-337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.05.032
Al-Qaim, F. F.; Abdullah, M. P.; Othman, M. R.; Khalik, W.A.N.M.A.W.A.N. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2014, 12, 62-72.
Mussa, Z. H.; Al-Qaim, F. F.; Othman, M. R.; Abdullah, M. P. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3338-3347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.07.006
Mussa, Z. H.; Al-Qaim, F. F.; Yuzir, A.; Hara, H.; Azman, S.; Chelliapan, S. Catalysts 2018, 8, 540-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8110540
Al-Qaim, F. F.; Mussa, Z. H.; Yuzir, A.; Abdullah, M. P.; Othman, M. R. J. Brazil. Chem. Soc. 2018, 29, 1721-1731. https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20180047 DOI: https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20180047

Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.