The Potential of Green as well as Roasted Coffee Water Extracts as in-vitro Inhibitors of Beta-Hematin Formation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v70i1.2474Keywords:
Coffee, HPLC, antimalarial activity, β-hematinAbstract
Abstract. This study investigates the antimalarial potential of coffee extracts exploring their relationship with roasting, absorption, effectiveness, and hemozoin production, while also identifying flavonoids and phenolic compounds. Research on the antimalarial properties of coffee extracts is crucial for developing new therapies. Coffee extracts could provide a natural and accessible source and understanding the effects of the roasting process can optimize their efficacy. Water extracts were obtained from both green and roasted coffee beans subjected to varying roasting times.
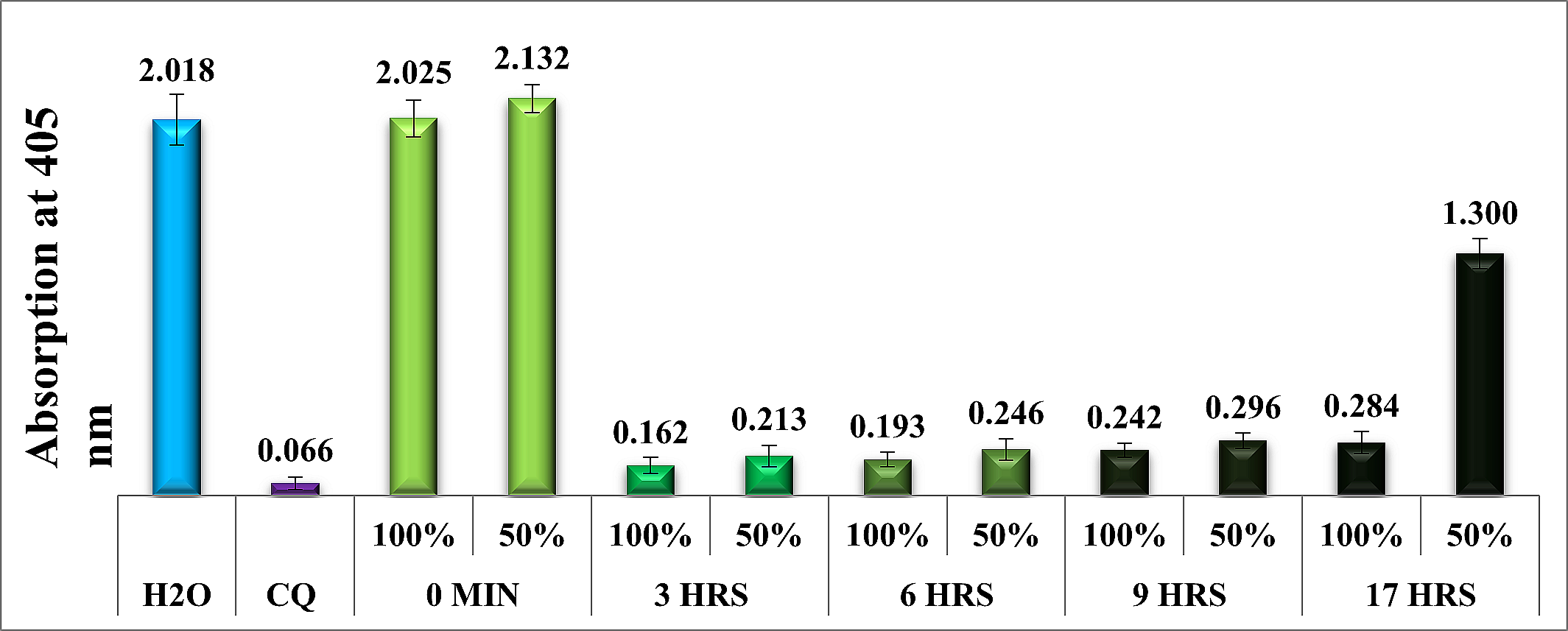
The effectiveness of the extracts was measured by the absorption of dissolved β- hematin at a wavelength of 405 nm. Chromatographic analysis using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was employed to separate and detect flavonoids and phenolic compounds within the extracts. Specific compound identification was achieved by comparing retention times and UV spectrum wavelengths of standards and samples. The study found that the absorption of coffee extracts was inversely correlated with their effectiveness, indicating that lower absorption corresponds to higher effectiveness. Green coffee water extracts exhibited limited efficacy, while roasted extracts demonstrated the highest efficacy. Chromatographic analysis identified flavonoids and phenolic compounds. Overall, the study reveals the antimalarial potential of coffee extracts, with extract effectiveness inversely related to absorption and inhibitory effects on hemozoin production. Chrysin as well as Galangin were identified as key constituents, highlighting their potential in antimalarial therapies. Further research is needed to understand their mechanisms of action.
Resumen. Este estudio se investigó el potencial antipalúdico de los extractos de café, explorando su relación con el tostado, la absorción, la eficacia y la producción de hemozoína, a la vez que se identificaron flavonoides y compuestos fenólicos. La investigación sobre las propiedades antipalúdicas de los extractos de café es crucial para el desarrollo de nuevas terapias. Los extractos de café podrían proporcionar una fuente natural y accesible, y comprender los efectos del proceso de tostado puede optimizar su eficacia. Se obtuvieron extractos acuosos de granos de café verde y tostado, sometidos a diferentes tiempos de tostado. La eficacia de los extractos se midió mediante la absorción de β-hematina disuelta a una longitud de onda de 405 nm. Se empleó un análisis cromatográfico mediante cromatografía líquida de alta resolución (HPLC) para separar y detectar flavonoides y compuestos fenólicos en los extractos. La identificación de compuestos específicos se logró comparando los tiempos de retención y las longitudes de onda del espectro UV de los estándares y las muestras. Se determinó que la absorción de los extractos de café está inversamente correlacionada con su eficacia, lo que indica que una menor absorción corresponde a una mayor eficacia. Los extractos de agua de café verde mostraron una eficacia limitada, mientras que los extractos tostados demostraron la mayor eficacia. Mediante el análisis cromatográfico se identificaron flavonoides y compuestos fenólicos. En general, el estudio revela el potencial antipalúdico de los extractos de café, cuya eficacia está inversamente relacionada con la absorción y los efectos inhibidores sobre la producción de hemozoína. La crisina y la galangina se identificaron como componentes clave, lo que destaca su potencial en terapias antipalúdicas. Futuras investigaciones deberán enfocarse en la comprensión de sus mecanismos de acción.
Downloads
References
1. Olafson, K.N.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Rimer, J.D.; Vekilov, P.G. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2017, 114, 7531-7536. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1700125114
2. Ma, W.; Balta, V.A.; Pan, W.; Rimer, J.D.; Sullivan, D.J.; Vekilov, P.G. Commun Bio. 2023, 6, 783. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-023-05046-z
3. Damiani, C.; Soler, F.; Le Govic; Y., Totet; A., Bentzinger, G.; Bouchut, A.; Mustière, R.; Agnamey, P.; Dassonville-Klimpt, A.; Sonnet, P. Microorganisms. 2024, 12, 2524. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122524
4. Sandlin, R.D.; Fong, K.Y.; Wicht, K.J.; Carrell, H.M.; Egan, T.J.; Wright, D.W. Inter J Parasit – Drugs & Drug Resist. 2014, 4,316-25. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpddr.2014.08.002
5. Abiodun, O.A.; Oladepo, O.M. Acta Pharm Sci. 2018, 56, 61. DOI: https://doi.org/10.23893/1307-2080.APS.05618
6. World malaria report 2022. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2022. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. 2022.
7. Akkawi, M.; Abu-Lafi, S.; Abu-Remeleh, Q.; Lutgen, P. Pharm Pharmacol Inter J. 2021, 9, 11-15. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15406/ppij.2021.09.00319
8. Akkawi, M.; Jaber, S.; Abu-Lafi, S.; Qutob, M.; Abu-Rmeleh, Q.; Lutgen, P. Mal World J. 2014, 5, 1-5.
9. Akkawi, M.; Abbasi, I.; Jaber, S.; Aburemeleh, Q.; Naseredin, A.; Lutgen, P. Brit. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 5, 156-162.
10. Akkawi, M.; Jaber, S.; Abu-Remeleh, Q.; Engeu, O.P.; Lutgen, P. Med. Aromat Plants. 2014, 3, 1000150. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.4172/2167-0412.1000150
11. Abu-Lafi, S.; Akkawi, M.; Abu-Remeleh, Q.; Jaber, S.; Qutob, M.; Lutgen, P. Pure. Pharm. Pharmacol. Inter J. 2018, 6, 4-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.15406/ppij.2018.06.00145
12. Jaber, S.; Abu-Lafi, S.; Lutgen, P.; Qutob, M.; Qassem Abu-Remeleh, Q.; Akkawi, M. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 3, 63-72. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.17265/2328-2150/2015.02.003
13. Blauer, G.; Akkawi, M. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2002, 398, 7-11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/abbi.2001.2638
14. Kumar, S.; Guha, M.; Choubey, V.; Maity, P.; Bandyopadhyay, U. Life Sci. 2007, 6, 80(9):813-28. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2006.11.008
15. Attieh, H.A.; Abu-Lafi, S.; Jaber S.; Abu-Remeleh Q.; Lutgen P.; Akkawi M. J. Med. Plants. Res. 2015, 9,998-1005. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5897/JMPR2015.5931
16. Inbaneson, S.J.; Sundaram, R.; Suganthi P. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2012, 5, 103-106. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1995-7645(12)60004-2
17. Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar, M.; Hosseinzadeh H. Iran J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 1100-1112. DOI: https://doi.org/10.22038/ijbms.2020.45269.10541
18. Shalayel, M.H.F.; Al-Mazaideh G.M.; Alanezi A.A.; Almuqati A.F.; Alotaibi M. Processes. 2023, 11, 1277. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041277
19. Shalayel, M.H.F.; Al-Mazaideh, G.M.; Alanezi, A.A.; Almuqati, A.F.; Alotaibi, M. Pharmaceuticals. 2023, 16, 704. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16050704
20. Al-Rawajfeh, A.E.; Alzalabieh, E.; Al Bazedi, G.; Al-Mazaideh, G.M.; Shalayel, M.H.F. Desal. Water Treat. 2023, 290, 46-55. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2023.29482
21. Abdelbagi, M.E.M.; Al-Mazaideh, G.M.; Ahmed, A.E.; Al-Rimawi, F.; Ayyal Salman, H.; Almutairi, A.; Abuilaiwi, F.A.; Wedian, F. Processes. 2023, 11, 1478. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11051478
22. Abdelbagi, M.E.M.; Al-Mazaideh, G.M.; Ahmed, A.E.; Al-Rimawi, F.; Ayyal Salman, H.; Almutairi, A.; Abuilaiwi, F.A.; Wedian, F. Processes. 2023, 11, 1955. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11071955
23. Khalid, M.; Amayreh, M.; Sanduka, S.; Salah, Z.; Al-Rimawi, F.; Al-Mazaideh, G.M.; Alanezi, A.A.; Wedian, F.; Alasmari, F.; Shalayel, M.H.F. Heliyon. 2022, 28, e10477. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10477. PMID: 36105455; PMCID: PMC9465121.
24. Jamhour, R.M.A.Q.; Al-Nadaf, A.H.; Wedian, F.; Al-Mazaideh, G.M.; Mustafa, M.; Huneif, M.A.; Mahmoud, S.Y.; Farrag, E.S.; Al-Rimawi, F.; Salman, H.A.; Alqudah, A.A.; Alakhras, F. Russ J Phys Chem A. 2022, 96, 1589–97. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024422070251
25. Al-Mazaideh, G.M.; Al-Mustafa, A.H.; Alnasser, S.M.A.; Nassir-Allah, I.; Tarawneh, K.A.; Al-Rimawi, F.; Mohamad Ibrahim, M.N.; Huneif, M.A.; Alshammari, S.O.; Yaqoob, A.A.; Wedian, F.; Shalayel, M.H.F. Heliyon. 2022, 8, e11516. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11516
26. Shalayel, M.H.F.; Nour, S.; Al-Mazaideh, G.M.; Mahmoud, S.Y.; Farrag, E.S. Med Sci. 2021, 25, 744-750.
27. Deharo, E.; García, R.N.; Oporto, P.; Gimenez, A.; Sauvain, M.; Jullian, V.; Ginsburg, H. Exp Parasitol. 2002, 100, 252-6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-4894(02)00027-9
28. Alves, R.C.; Casal S.; Alves M.R.; Oliveira M.B. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 295-299. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.08.093
29. Santos, É.M.d.; Macedo, L.M.d.; Tundisi, L.L.; Ataide, J.A.; Camargo, G.A.; Alves, R.C.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Mazzola, P.G. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 280-91. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.02.064
30. Nassar, M.O.; El-Sayed, H.M.; Kobisi, A.A.E.N. J. Pharm. Res. Inter. 2019, 31, 1-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.9734/jpri/2019/v31i130290
31. Rawangkan, A.; Siriphap, A.; Yosboonruang, A.; Kiddee, A.; Pook-In, G.; Saokaew, S.; Sutheinkul, O.; Duangjai, A. Front Nutrit. 2022, 9, 865684. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.865684
32. Alamri, E., Rozan, M.; Bayomy, H. Saudi J. Biol Sci. 2022, 29, 3133-3139. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.03.025
33. Franca, A.S.; Mendonça, J.C.F.; Oliveira, S.D. LWT - Food Sci Tech. 2005, 38, 709-715. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2004.08.014
34. Sualeh, A.; Tolessa, K.; Mohammed, A. Heliyon. 2020, 6, e05812. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05812
35. Wang, H.Y.; Qian, H.; Yao, W.R. Food Chemt. 2011, 128, 573-584. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.03.075
36. Bergamaschi, M.; Simoncini, N.; Spezzano, V.M.; Ferri, M.; Tassoni, A. Foods. 2023, 12, 1264. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061264
37. Ribeiro, E.; Rocha, T.S.; Prudencio, S.H. Food Chem. 2021, 348, 129061. 20210111. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129061
38. Coronado, L.M.; Nadovich, C.T.; Spadafora, C. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2014, 1840, 2032-41. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.02.009
39. Spiegel, M. J. Org. Chem. 2024, 89, 8676-90. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.4c00611
40. Tuli, H.S.; Sak, K.; Adhikary, S.; Kaur, G.; Aggarwal, D.; Kaur, J.; Kumar, M.; Parashar, N.C.; Parashar, G.; Sharma, U.; Jain, A. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood). 2022, 247, 345-359. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/15353702211062510
41. Jan, R., & Mead, J. R. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 259, 153–157. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00263.x
42. Ittadwar, P.A.; Puranik, P.K. Inter. J. Pharm. Sci. Drug. Res. 2021, 13, 457–469. DOI: https://doi.org/10.25004/IJPSDR.2021.130502
43. Lin, K.; Fu, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhu C. Korean J. Pain. 2024, 37, 151-163. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.23363
44. Mead, J.; McNair, N. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 259, 153–157. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00263.x
45. Gong, M.; Xia, X.; Chen, D.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiang, H.; Li, X.; Zhi, Y.; Mo, Y. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1278997. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2023.1278997
46. Jung, S.; Kim, M.H.; Park, J.H.; Jeong, Y.; Ko, K.S. J. Med. Food. 2017, 20, 626-635. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2017.3935
47. Castaldo, L.; Toriello, M.; Sessa, R.; Izzo, L.; Lombardi, S.; Narváez, A.; Ritieni A.; Grosso, M. Nutrients. 2021, 13, 4368. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124368

Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mutaz Akkawi; Fuad Al-Rimawi; Qassem Abu-Remeleh, Latifah Al Shammari, Amal N. Alanazi, Salma Saddeek, Fadel Wedian, Ghassab M. Al-Mazaideh, Mohammed Helmy Faris Shalayel

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.