Computational Study of New Isatin Molecules as Potential Thymidine Phosphorylase (TP) Inhibitors Against Cancer Activity. 3D-QSAR, Molecular Docking, ADME-Tox, And Molecular Dynamics Simulation Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v69i4.2150Keywords:
Cancer, isatin, molecular modeling, thymidine phosphorylase (TP)Abstract
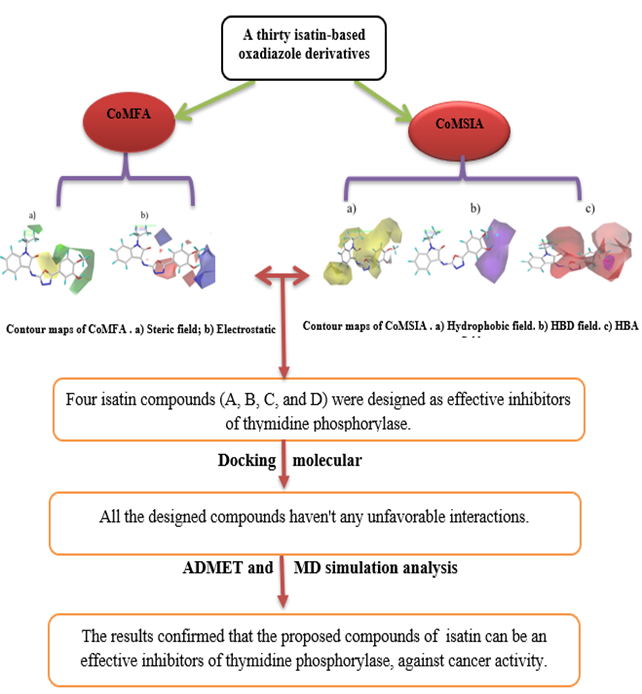
Abstract. The quenching of TP enzyme activity helps treat and control diseases. In this research, computational methods investigated a series of thirty isatin-based oxadiazoles as potential TP inhibitors. 3D-QSAR was used to design four isatins (A, B, C, and D) derivatives with high anticancer activity. Molecular Docking was used to investigate interaction types between designed isatin derivatives (A, B, C, and D) and the TP enzyme (PDB: 4EAD); the results show that all compounds have several types of exciting interactions with no unfavorable interactions, but only compounds A and B have conventional hydrogen bond interactions as promising inhibition activity. The Binding Energy between (A, B, C, and D) compounds with TP enzyme were obtained by molecular dynamic simulation at 100 ns. A and B compounds had a more substantial binding free energy than C and D compounds, with binding energies of-20.1374 +/- 0.1189 kJ/mol, -20.1897 +/- 0.1333 kJ/mol, -18.1344 +/-0.1604 kJ/mol, and 19.077 +/-0.1549 kJ/mol, respectively. The pharmacokinetics of (A, B, C, and D) molecules were obtained by using ADMET predictions. Based on the above findings, the current work recommends four compounds as potential TP enzyme inhibitors that activate colorectal and breast cancers.
Resumen. La inhibición de la actividad de la enzima TP ayuda a tratar y controlar las enfermedades. En esta investigación, se utilizaron métodos computacionales para investigar una serie de treinta oxadiazoles basados en isatina como posibles inhibidores de TP. Se utilizó 3D-QSAR para diseñar cuatro derivados de isatinas (A, B, C y D) con alta actividad anticancerígena. Se utilizó el acoplamiento molecular para investigar los tipos de interacción entre los derivados de isatina diseñados (A, B, C y D) y la enzima TP (PDB: 4EAD); los resultados muestran que todos los compuestos tienen varios tipos de interacciones excitantes sin interacciones desfavorables, pero solo los compuestos A y B tienen interacciones de enlace de hidrógeno convencionales como actividad de inhibición prometedora. La energía de enlace entre los compuestos (A, B, C y D) y la enzima TP se obtuvo mediante simulación dinámica molecular a 100 ns. Los compuestos A y B tenían una energía libre de enlace más sustancial que los compuestos C y D, con energías de enlace de -20,1374 +/- 0,1189 kJ/mol, -20,1897 +/- 0,1333 kJ/mol, -18,1344 +/- 0,1604 kJ/mol y 19,077 +/- 0,1549 kJ/mol, respectivamente. La farmacocinética de las moléculas (A, B, C y D) se obtuvo mediante predicciones ADMET. Con base en los hallazgos anteriores, recomendamos considerar cuatro compuestos como posibles inhibidores de la enzima TP que activan los cánceres colorrectales y de mama.
Downloads
References
References
Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D. M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F.. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136 (5), E359–E386. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29210.
Nagai, H.; Kim, Y. H. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9 (3), 448–451. https://doi.org/10.21037/jtd.2017.02.75.
Bronckaers, A.; Gago, F.; Balzarini, J.; Liekens, S. Med. Res. Rev. 2009, 29 (6), 903–953. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.20159.
Akiyama, S.; Furukawa, T.; Sumizawa, T.; Takebayashi, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Shimaoka, S.; Haraguchi, M.. Cancer Sci. 2004, 95 (11), 851–857. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2004.tb02193.x.
Elamin, Y. Y.; Rafee, S.; Osman, N.; O′Byrne, K. J.; Gately, K. Cancer Microenviron. 2016, 9 (1), 33–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-015-0173-y.
Walko, C. M.; Lindley, C.. Ther. 2005, 27 (1), 23–44.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2005.01.005.
Meropol, N. J.; Gold, P. J.; Diasio, R. B.; Andria, M.; Dhami, M.; Godfrey, T.; Kovatich, A. J.; Lund, K. A.; Mitchell, E.; Schwarting, R. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24 (25), 4069–4077. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2005.05.2084.
Han, J.-Y.; Hong, E. K.; Lee, S. Y.; Yoon, S. M.; Lee, D. H.; Lee, J. S. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 58 (6), 650–654. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.2004.022764.
Javid, M. T.; Rahim, F.; Taha, M.; Nawaz, M.; Wadood, A.; Ali, M.; Mosaddik, A.; Shah, S. A. A.; Farooq, R. K. Bioorganic Chem. 2018, 79, 323–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.05.011.
Sridhar, S. K.; Ramesh, A. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 24 (10), 1149–1152. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.24.1149.
Selvam, P.; Murugesh, N.; Chandramohan, M.; Debyser, Z.; Witvrouw, M. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 70 (6), 779–782. https://doi.org/10.4103/0250-474X.49121.
Rohini, R.; Reddy, P. M.; Shanker, K.; Kanthaiah, K.; Ravinder, V.; Hu, A. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34 (7), 1077–1084. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0705-z.
Verma, M.; Pandeya, S. N.; Singh, K. N.; Stables, J. P. Acta Pharm. Zagreb Croat. 2004, 54 (1), 49–56.
Raj, R.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P. J.; Kumar, V. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24 (3), 756–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.12.109.
Bharathi Dileepan, A. G.; Daniel Prakash, T.; Ganesh Kumar, A.; Shameela Rajam, P.; Violet Dhayabaran, V.; Rajaram, R. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2018, 183, 191–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.04.029.
Zhang, M.-Z.; Chen, Q.; Yang, G.-F.. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 89, 421–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.10.065.
Guo, H. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 164, 678–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.12.017.
Ibrahim, H. S.; Abou-Seri, S. M.; Tanc, M.; Elaasser, M. M.; Abdel-Aziz, H. A.; Supuran, C. T Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 103, 583–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.09.021.
Eldehna, W. M.; Altoukhy, A.; Mahrous, H.; Abdel-Aziz, H. A. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 90, 684–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.12.010.
Sharma, P.; Senwar, K. R.; Jeengar, M. K.; Reddy, T. S.; Naidu, V. G. M.; Kamal, A.; Shankaraiah, N. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 104, 11–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.09.025.
Kerzare, D.; Khedekar, P. J. Pharm. Biosci. Res. 2016, No. 6, 144–156.
Erdmann, O. L. J. Für Prakt. Chem. 1840, 19 (1), 321–362. https://doi.org/10.1002/prac.18400190161.
Silva, J. F. M. da; Garden, S. J.; Pinto, A. C. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2001, 12, 273–324. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-50532001000300002.
Bergman, J.; Lindström, J.-O.; Tilstam, U. Tetrahedron 1985, 41 (14), 2879–2881. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4020(01)96609-8.
Klebe, G.; Abraham, U.; Mietzner, T. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37 (24), 4130–4146. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm00050a010.
Cramer, R. D.; Patterson, D. E.; Bunce, J. D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110 (18), 5959–5967. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00226a005.
El-Mernissi, R.; El Khatabi, K.; Khaldan, A.; ElMchichi, L.; Shahinozzaman, M.; Ajana, M. A.; Lakhlifi, T.; Bouachrine, M. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2021, 66 (1). https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v66i1.1578.
EL-Mernissi, R.; EL Khatabi, K.; Khaldan, A.; El Mchichi, L.; Ajana, M. A.; Lakhlifi, T.; Bouachrine, M. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 7608–7614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.03.080.
Clark, M.; Cramer, R. D.; Van Opdenbosch, N. Comput. Chem. 1989, 10 (8), 982–1012. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.540100804.
Purcell, W. P.; Singer, J. A. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1967, 12 (2), 235–246. https://doi.org/10.1021/je60033a020.
Golbraikh, A.; Tropsha, A. Mol. Graph. Model. 2002, 20 (4), 269–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1093-3263(01)00123-1.
Golbraikh, A.; Tropsha, A. Mol. Graph. Model. 2002, 20 (4), 269–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1093-3263(01)00123-1.
Roy, P. P.; Leonard, J. T.; Roy, K. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2008, 90 (1), 31–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2007.07.004.
Edache, E. I.; Uzairu, A.; Mamza, P. A.; Shallangwa, G. A. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2022, 66 (4). https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v66i4.1726.
Ibrahim, M. T.; Uzairu, A.; Umar, A. B.; Bello, A. S.; Isyaku, Y. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2019, 64 (1). https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v64i1.1025
DeLano, W. L. DeLano. PyMOL Mol. Graph. Syst. DeLano Sci. San Carlos CA USA 2002
Discovery Studio Predictive Science Application | Dassault Systèmes BIOVIA https://www.3dsbiovia.com/products/collaborative-science/biovia-discovery-studio/ (accessed Feb 6,2020).
Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7 (1), 42717. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42717.
El Khatabi, K.; Kumar, S.; El-Mernissi, R.; Singh, A. K.; Ajana, M. A.; Lakhlifi, T.; Bouachrine, M. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 0 (0), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2022.2134210.
Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A. E.; Berendsen, H. J. C. GROMACS: Fast, Flexible, and Free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26 (16), 1701–1718. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20291.
Boonstra, S.; Onck, P. R.; Giessen, E. van der. CHARMM TIP3P Water Model Suppresses Peptide Folding by Solvating the Unfolded State. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120 (15), 3692–3698. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.6b01316.
El-Mernissi, R.; El Khatabi, K.; Khaldan, A.; Elmchichi, L.; Shahinozzaman, M.; Ajana, M.; Lakhlifi, T.; Bouachrine, M. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2021, 66, 79–94. https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v66i1.1578.
Lee, S.; Tran, A.; Allsopp, M.; Lim, J. B.; Hénin, J.; Klauda, J. B. CHARMM36 United Atom Chain Model for Lipids and Surfactants. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118 (2), 547–556. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp410344g.
Hayes, J. M.; Skamnaki, V. T.; Archontis, G.; Lamprakis, C.; Sarrou, J.; Bischler, N.; Skaltsounis, A.-L.; Zographos, S. E.; Oikonomakos, N. G. Funct. Bioinforma. 2011, 79 (3), 703–719. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.22890.
El-Mernissi, R.; El khatabi, K.; Khaldan, A.; Bouamrane, S.; ElMchichi, L.; Aziz Ajana, M.; Lakhlifi, T.; Bouachrine, M. Orbital Electron. J. Chem. 2022, 14 (1), 24–32. https://doi.org/10.17807/orbital.v14i1.1659.
Tong, J.-B.; Feng, Y.; Wang, T.-H.; Luo, D. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2021, 49 (4), e21046–e21054. https://doi.o DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2040(21)60095-6

Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Reda EL-Mernissi, Marwa Alaqarbeh, Ayoub Khaldan, Abdelouahid Sbai, Mohammed Aziz Ajana, Tahar Lakhlifi, Mohammed Bouachrine

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.









