Metformin Adsorption on Binuclear Boron Schiff Complexes
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v69i3.2207Keywords:
Binuclear boron Schiff complexes, metformin, adsorption, DFTAbstract
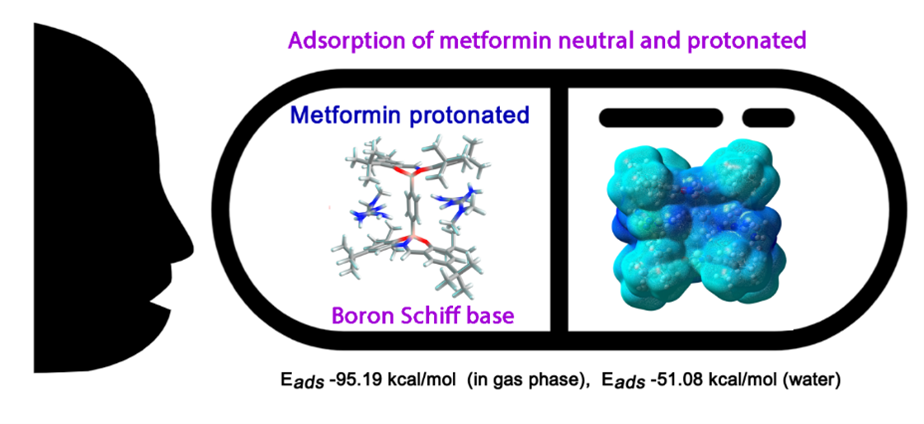
Abstract. Metformin (N, N-dimethylbiguanidine) is a drug with many biological functions. In certain cases, it is necessary for this compound to interact with some molecules in order to increase the efficacy of administration in the human body. For this purpose, density functional theory was used to study the intermolecular interactions between binuclear boron Schiff complexes and metformin (charged and neutral). All structures herein, have been studied by using Natural and Mulliken charges, Natural Bond Orbitals (NBO), and quantum molecular descriptors. The adsorption energies (Eads) for the most stable structures with neutral metformin are -27.02 to -53.34 kcal/mol in gas phase. The Eads for two monoprotonated metformin shows -39.71 kcal/mol in gas phase and -84.08 kcal/mol in water. The NBO results showed that the donor orbitals belong to the nitrogen atoms of metformin, while the acceptor orbitals belong to the C-H atoms of tert-butyl groups in binuclear boron Schiff complexes. The binuclear structure could be used as an adsorber and as a carrier of metformin molecules.
Resumen. La metformina(N,N-dimetilbiguanidina) es un fármaco con múltiples funciones biológicas. En ciertos casos, es necesario que este compuesto interactúe con ciertas moléculas para aumentar la eficacia de su administración en el cuerpo humano. Para ello, se empleó la teoría del funcional de la densidad para estudiar las interacciones intermoleculares entre los complejos de Schiff de boro binucleares y la metformina (con carga y neutra). Todas las estructuras aquí descritas se han estudiado utilizando cargas naturales y de Mulliken, orbitales de enlace naturales (NBO) y descriptores moleculares cuánticos. Las energías de adsorción (Eads) para la mayoría de las estructuras estables con metformina neutra son de -27.2 a -53.34 kcal/mol en fase gaseosa. Las Eads para dos metforminas monoprotonadas muestran -39.71 kcal/mol en fase gaseosa y -84.08 kcal/mol en agua. Los resultados del NBO mostraron que los orbitales donantes pertenecen a los átomos de nitrógeno de la metformina, mientras que los orbitales aceptores pertenecen a los átomos C-H de los grupos ter-butilos en los complejos de Schiff de boro binucleares. La estructura binuclear podría utilizarse como adsorbente y transportador de moléculas de metformina.
Downloads
References
Dunn, C. J.; Peters, D. H. Drugs. 1995, 49, 721-749. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199549050-00007
Wang, Y. W.; He, S. J.; Feng, X.; Cheng, J.; Luo, Y. T.; Tian, L.; Huang, Q. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 2421-2429. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S141675
Shurrab, N. T.; Arafa, E. S. A. Obes. Med. 2020, 17, 100186. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100186
Samuel, V. P.; Dahiya, R.; Singh, Y.; Gupta, G.; Sah, S. K.; Gubbiyappa, S. K.; Chellappan, D. K.; Dua, K. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2019, 38, 133-141. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1615/JEnvironPatholToxicolOncol.2019029388
Yu, H.; Zhong, X.; Gao, P.; Shi, J.; Wu, Z.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Song, Y. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2019, 10, 617. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00617
Landman, G. W.; Kleefstra, N.; Hateren, K. J. van; Groenier, K. H.; Gans, R. O.; Bilo, H. J. Diabetes care. 2010, 33, 322-326. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2337/dc09-1380
Song, R. Diabetes care. 2016, 39, 187-189. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2337/dci15-0013
Kim, A.; Mujumdar, S. K.; Siegel, R. A. Chemosensors. 2014, 2, 1-12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors2010001
Raju, D. B.; Sreenivas, R.; Varma, M. M. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2010, 2, 274-278 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5005/jp/books/11432_8
Graham, G. G.; Punt, J.; Arora, M.; Day, R. O.; Doogue, M. P.; Duong, J.; Furlong, T. J.; Greenfield, J. R.; Greenup, L. C.; Kirkpatrick, C. M.; Ray, J. E.; Timmins, P.; Williams, K. M. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2011, 50, 81-98. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/11534750-000000000-00000
Chen, Y.; Shan, X.; Luo, C.; He, Z. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 219-230. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-020-00480-1
Meka, V. S.; Gorajana, A.; Dharmanlingam, S. R.; Kolapalli, V. R. Invest. Clin. 2013, 54, 347-459.
Kamali, F.; Rajaei, G. E.; Mohajeri, S.; Shamel, A.; Khodadadi-Moghaddam, M. Monatsh. Chem. 2020, 151, 711-720. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-020-02597-3
Rebitski, E. P.; Darder, M.; Sainz-Diaz, C. I.; Carraro, R.; Aranda, P.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E. Appl. Clay. Sci. 2020, 186, 105418. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2019.105418
Mirzaei, M.; Gulseren, O.; Jafari, E.; Aramideh, M. Iran. Chem. Commun. 2019, 1, 334-343.
Ghasemi, A. S.; Taghartapeh, M. R.; Soltani, A.; Mahon, P. J. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 275, 955-967. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.11.124
Haddish-Berhane, N.; Rickus, J. L.; Haghighi, K. Int. J. Nanomedicine. 2007, 2, 315- 331.
Rangel, V. N.; Delgadillo, A. N.; Salas, A. C. J. Nanomed. Res. 2015, 2, 23.
Molina-Paredes, A. A.; Jiménez-Pérez, V. M.; Lara-Cerón, J. A.; Moggio, I.; Arias, E.; Santillán, R.; Sánchez, M.; Saucedo-Yañez, A.; Muñoz-Flores, B. M. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 2019, 33, e4609; DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4609
Ibarra-Rodríguez, M.; Muñoz-Flores, B. M.; Gómez-Treviño, A.; Chan-Navarro, R.; Berrones-Reyes, R. J.; Chávez-Reyes, A.; Dias, H. V. R.; Sánchez Vázquez, M.; Jiménez-Pérez, V. M. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 2019, 33, e4718. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4718
Ibarra-Rodrı́guez, M.; Muñoz-Flores, B. M.; Dias, H.V. R.; Sánchez, M.; Gomez- Treviño, A.; Santillan, R.; Farfán, N.; Jiménez-Pérez, V. M. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 2375-2385. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.6b02802
Hoseininezhad-Namin, M. S.; Pargolghasemi, P.; Alimohammadi, S.; Rad, A. S.; Taqavi, L. Physica E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2017, 90, 204-213. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2017.04.002
Gang, L.; Guo, S.; Wu, Q.; Wu, L. Mol. Phys. 2020, 118, e1788190. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00268976.2020.1788190
Delgadillo Armendariz, N. L.; Rangel Vásquez, N. A.; Marquez Brazón, E. A. Rev. Colomb. Quim. 2020, 49, 12-17. DOI: https://doi.org/10.15446/rev.colomb.quim.v49n2.84723
Fakhari, S.; Nouri, A.; Jamzad, M.; Arab-Salmanabadi, S.; Falaki, F. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2021, 68, 67-75. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jccs.202000304
Arshad, M.; Arshad, S.; Majeed, M. K.; Frueh, J.; Chang, C.; Bilal, I.; Niaz, S. I.; Khan, M. S.; Tariq, M. A.; Yasir Mehboob, M. ACS Omega. 2023, 8, 11318-11325. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.3c00058
Perdew, J. P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865-3868.
Krishnan, R.; Binkley, J. S.; Seeger, R.; Pople, J. A. J. Phys. Chem. 1980, 72, 650-654. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.438955
Stefan, G.; Jens, A.; Stephan, E.; Helge, K. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104.
Glendening, E. D.; Landis, C. R.; Weinhold, F. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 1429- 1437. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.23266
Perdew, J. P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 77, 3865-3868. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.3865
Pritchard, B. P.; Altarawy, D.; Didier, B.; Gibson, T. D.; Windus, T. L. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 4814-4820. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00725
Parr, R. G.; Pearson, R. G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 7512-7516. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00364a005
Parr, R. G.; Donnelly, R. A.; Levy, M.; Palke, W. E. J. Chem. Phys. 1978, 68, 3801- 3807. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.436185
Parr, R. G.; Szentpály, L. V.; Liu, S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 1922-1924. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja983494x
Janaki, C. S.; Sailatha, E.; Gunasekaran, S.; Kumaar, G. R. Int. J. TechnoChem. Res. 2016, 91-104.
Jeffrey, G.A., in: An introduction to hydrogen bonding, Oxford University Press: New York and Oxford., 1997.
Cordero, B.; Gómez, V.; Platero-Prats, A. E.; Revés, M.; Echeverría, J.; Cremades, E.; Barragán, F.; Alvarez, S. Dalton Trans. 2008, 2832-2838. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/b801115j
Dannenberg, J. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 5604-5604. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja9756331
Yu, J.; Su, N. Q.; Yang, W. JACS Au. 2022, 2, 1383-1394. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacsau.2c00085
Weinhold, F.; Landis, C. R., in: Valency and bonding: a natural bond orbital donor- acceptor perspective, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2005.
Hernández, B.; Pflüger, F.; Kruglik, S. G.; Cohen, R; Ghomi, M.; J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 114, 42-48. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2015.04.041
Mondal, S.; Samajdar, R. N.; Mukherjee, S.; Bhattacharyya, A. J.; Bagchi, B. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 2227-2242. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.7b11928

Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Marisol Ibarra-Rodríguez, Víctor Víctor Jiménez Pérez, Blanca M. Muñoz-Flores, Mario Sánchez

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.