pH Determination Under Unconventional Conditions of Temperature and Ionic Strength
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v69i2.2160Keywords:
Chemical equilibria, apparent constant, pH determination, Van’t Hoff, Debye-HückelAbstract
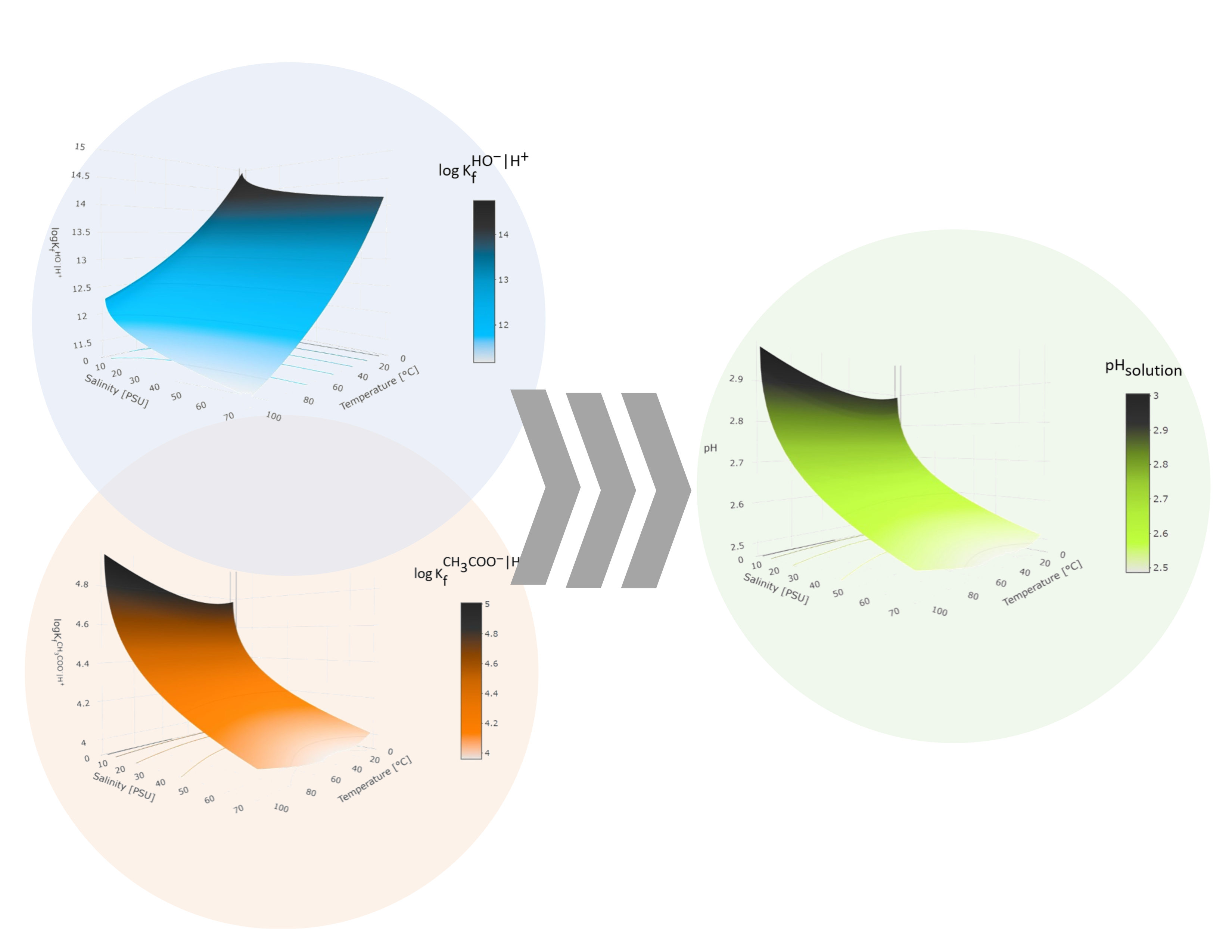
Abstract. The pH in an aqueous solution is a relevant parameter in many fields of chemistry, and its determination is not trivial when factors such as temperature and ionic strength are considered. In multicomponent systems, this situation becomes significant. Even in simple systems, there are variations of up to 1.813 pH units in CH3COOK solutions when thermodynamic constants are used instead of apparent constants to calculate it. In this study, we propose a methodology that investigates the influence of these variables on the apparent dissociation constants of water and acetic acid, as well as their impact on the pH measurement of solutions prepared from CH3COOH and a salt of its conjugate base. Non−linear adjustments were carried out using a polynomial analogous to the Van't Hoff equation to establish a relationship between the thermodynamic constants of formation and the wide temperature range proposed. Furthermore, the influence of the ionic medium was considered when correcting the activity coefficients using the extended model of the Debye−Hückel equation. This approach enabled a detailed description of the set of apparent formation constants, which were directly applied in the formal pH calculation without approximations. These variations were represented on response surfaces and interpolated to the proposed operating conditions. The successful correlation between the theoretical results and those obtained experimentally through potentiometric measurements confirmed a harmonious relationship between both data sets. The described methodology offers a novel alternative for calculating pH in multicomponent systems, including real samples, in unconventional conditions of temperature and ionic strength.
Resumen. El pH en una disolución acuosa es un parámetro relevante en muchos campos de la química, y su determinación no es trivial cuando se consideran factores como la temperatura y la fuerza iónica. En sistemas multicomponente, esta situación se vuelve significativa. Incluso en sistemas simples, existen variaciones de hasta 1.813 unidades de pH en disoluciones de CH3COOK cuando se utilizan constantes termodinámicas en lugar de constantes aparentes para calcularlo. En este trabajo, se propone una metodología que indaga en la influencia de estas variables sobre las constantes de disociación aparentes del agua y del ácido acético, así como su impacto en la medición del pH de soluciones preparadas a partir de CH3COOH y una sal de su base conjugada. Se realizaron ajustes no lineales utilizando un polinomio análogo a la ecuación de Van't Hoff para establecer una relación entre las constantes termodinámicas de formación y el amplio rango de temperaturas propuesto. Además, se consideró la influencia del medio iónico al corregir los coeficientes de actividad mediante el modelo extendido de la ecuación de Debye−Hückel. Este enfoque permitió una descripción detallada del conjunto de constantes de formación aparentes, que se aplicaron directamente en el cálculo formal del pH sin aproximaciones. Estas variaciones se representaron en superficies de respuesta y se interpolaron a las condiciones de operación propuestas. La correlación exitosa entre los resultados teóricos y los obtenidos experimentalmente mediante mediciones potenciométricas confirmó una relación armoniosa entre ambos conjuntos de datos. La metodología descrita ofrece una alternativa novedosa para el cálculo del pH en sistemas multicomponentes, incluidas muestras reales, en condiciones no convencionales de temperatura y fuerza iónica.
Downloads
References
Buck, R. P.; Rondinini, S.; Covington, A. K.; Baucke, F. G. K.; Brett, C. M. A.; Camöes, M. F.; Milton, M. J. T.; Mussini, T.; Naumann, R.; Pratt, K. W.; Spitzer, P.; Wilson, G. S. Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 2169–2200. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1351/pac200274112169
Long, L.-S. CrystEngComm. 2010, 12, 1354–1365. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/b921146b.
Mayes, W. M.; Batty, L. C.; Younger, P. L.; Jarvis, A. P.; Kõiv, M.; Vohla, C.; Mander, U. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3944–3957. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.06.045.
Pierson, T. C.; Diamond, M. S. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 168–175. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coviro.2012.02.011.
Tao, W.; Wang, J.; Parak, W. J.; Farokhzad, O. C.; Shi, J. ACS Nano. 2019, 13, 4876–4882. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b01696.
Śmigiel, W. M.; Lefrançois, P.; Poolman, B. Top. Life Sci. 2019, 3, 445–458. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/etls20190017.
Abdella, S.; Abid, F.; Youssef, S. H.; Kim, S.; Afinjuomo, F.; Malinga, C.; Song, Y.; Garg, S. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2023, 28, 103414. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2022.103414.
Hendi, A.; Hassan, M. U.; Elsherif, M.; Alqattan, B.; Park, S.; Yetisen, A. K.; Butt, H. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 3887–3901. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.s245743.
Gigliuto, A.; Cigala, R. M.; Irto, A.; Felice, M. R.; Pettignano, A.; Milea, D.; Materazzi, S.; Stefano, C. D.; Crea, F. Biomolecules. 2021, 11, 1312. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11091312.
Soleimani, F.; Afshari, T.; Mokhtari, F.; Gharib, F. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2015, 83, 6–11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jct.2014.11.013.
Bellová, R.; Melicherčíková, D.; Tomčík, P. J. Chem. Educ. 2018, 95, 1548–1553. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.8b00086.
Clark, T. M.; Dickson-Karn, N. M.; Anderson, E. J. Chem. Educ. 2022, 99 (4), 1587–1595. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.1c00819.
Styn, R.; Holtz, A.; Biselli, A.; Kaminski, S.; Jupke, A. J. Solut. Chem. 2022, 51, 517–539. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-022-01146-2.
Ma, J.; Shu, H.; Yang, B.; Byrne, R. H.; Yuan, D. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2019, 1081, 18–31. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.06.024.
Millero, F. J.; Graham, T. B.; Huang, F.; Bustos-Serrano, H.; Pierrot, D. Mar. Chem. 2006, 100, 80–94. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2005.12.001.
Briones-Guerash-S. U.; García-Mendoza, A.; Aguilar-Cordero, J. C. J. Chem. Educ. 2023, 100, 4663–4673. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.3c00790.
Burgot, J. L., in: Ionic Equilibria in Analytical Chemistry, 1st ed.; Springer Science & Business Media, 2012. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-8382-4
Butler, J. N.; Cogley, D. R., in: Ionic Equilibrium: Solubility and pH Calculations, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1998.
Kahlert, H.; Scholz, F., in: Acid-Base Diagrams; Springer Science & Business Media, 2013. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-37902-4
Castellan, G. W., in: Physical Chemistry, 3rd ed.; 1983.
Martell, A. E.; Smith, R. M., in: Critical Stability Constants. Volume 2: Amines; Lenum Press, 1975; Vol. 2. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-4452-0.
Martell, A. E.; Smith, R. M., in: Critical Stability Constants. Volume 3: Other Organic Ligands; Springer Science+Business Media, 1977; Vol. 3. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-1568-2.
Martell, A. E.; Smith, R. M., in: Critical Stability Constants. Volume 4: Inorganic Complexes; Springer Science+Business Media, 1976; Vol. 4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-5506-0.
Martell, A. E.; Smith, R. M., in: Critical Stability Constants. Volume 5: First Supplement; Springer Science+Business Media, 1982; Vol. 5. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-6761-5
Martell, A. E.; Smith, R. M., in: Critical Stability Constants. Volume 6: Second Supplement; Springer Science+Business Media, 1989; Vol. 6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-6764-6.
Brown, P. L.; Ekberg, C., in: Hydrolysis of Metal Ions; John Wiley & Sons, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527656189
Atkins, P.; de Paula, J., in: Physical Chemistry, 9th ed.; W. H. Freeman and Company, 2014.
Gagliardi, L. G.; Castells, C. B.; Ràfols, C.; Rosés, M.; Bosch, E. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 2007, 52, 1103–1107. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/je700055p.
Helgeson, H. C.; Kirkham, D. H. Am. J. Sci. 1974, 274, 1199–1261. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2475/ajs.274.10.1199.
Fegley, B., in: Practical Chemical Thermodynamics for Geoscientists; Elsevier, 2013.
Khan, M. N.; Warrier, P.; Peters, C. J.; Koh, C. A. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 35, 1355–1361. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2016.03.092.
Burgot, J. L., in: The Notion of Activity in Chemistry, 1st ed.; Springer, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46401-5
Millero, F. J., in: Chemical Oceanography; CRC Press, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1201/b14753
Jouyban, A.; Soltanpour, S.; Chan, H.-K. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 269, 353–360. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2003.09.010.
Catenaccio, A.; Daruich, Y.; Magallanes, C. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2003, 367, 669–671. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2614(02)01735-9
Massel, S. R., in: Internal Gravity Waves in the Shallow Seas; Springer, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-18908-6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-18908-6_2
Marcus, Y. Chem. Rev. 2001, 88, 1475–1498. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00090a003
Jenkins, B.; Thankur, K. P. J. Chem. Educ. 1979, 56, 576–577. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ed056p576.
Roobottom, H. K.; Jenkins, H. D. B.; Passmore, J.; Glasser, L. J. Chem. Educ. 1999, 76, 1570. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ed076p1570.
Bandura, A. V.; N, L. S. The J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data. 2006, 35, 15–30. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1928231.
Hunter, K. A., in: Acid-base Chemistry of Aquatic Systems, 1999.
Brown, A. M. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2001, 65, 191–200. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-2607(00)00124-3
de Levie, R., in: How to Use Excel® in Analytical Chemistry and in General Scientific Data Analysis; Cambridge University Press, 2001. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511808265
Kiliç, E.; Aslan, N. Microchim. Acta. 2005, 151, 89–92. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-005-0380-1.
Harned, H. S.; Ehlers, R. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1933, 55, 652–656. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01329a027.
Gordus, A. A. J. Chem. Educ. 1991, 68 397. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ed068p397.
Trémillon, B., in: Chemistry in Non-Aqueous Solvents; D. Reidel Publishing Company: Boston, USA, 1974. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-2123-4.
Charlot, G.; Trémillon, B., in: Chemical Reactions in Solvents and Melts, First ed.; Harvey, D., Translator; Pergamon Press, 1969. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-012678-4.50017-8
Burke, J. D. J. Chem. Educ. 1976, 53, 79. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ed053p79.
Boisen, O.; Corral, A.; Pope, E.; Goeltz, J. C. J. Chem. Educ. 2019, 96, 1418–1423. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.8b00812.
Bard, A. J.; Faulkner, L. R., in: Electrochemical Methods; Wiley, 2000.

Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ricardo G. Martínez-Pérez, Emmanuel Ruiz-Villalobos, Fernando D. González-Arteaga, Elizabeth Vilchis-Barrera, Jorge Ruvalcaba-Juárez, Arturo Garcia-Mendoza

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.