Sesuvioside A from Gomphrena celosioides possesses the Dual Anti-gout Actions Via Anti-xanthine Oxidase and Anti-inflammatory Activities
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v69i4.2358Keywords:
Gomphrena celosioides Mart, sesuvioside A, xanthine oxidase (XO), anti-inflammatory, anti-goutAbstract
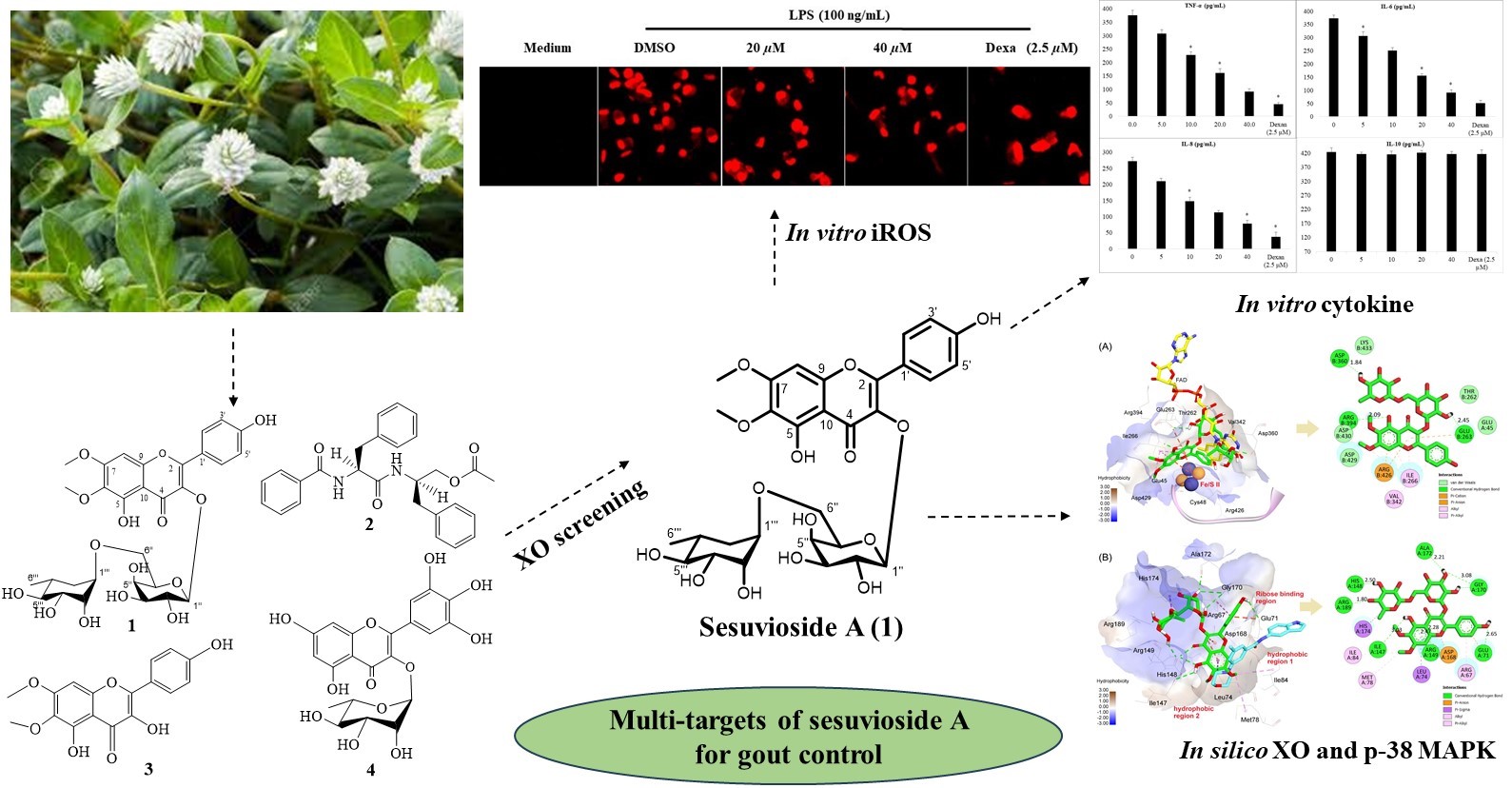
Abstract. Gomphrena celosioides Mart. has been widely used for the treatment of gout in Vietnam. A bio-guided isolation of xanthine oxidase inhibitors revealed that sesuvioside A, the main constituent in the butanol fraction of the aerial parts of G. celosioides, is a potential anti-gout compound. The anti-gout activity of sesuvioside A, a main constituent isolated from the butanol fraction for the first time was further extensively investigated using in vitro biological assays, including inhibition of xanthine oxidase (XO) activity, nitric oxide (NO), intracellular reactive oxygen species (iROS), pro-inflammatory cytokines productions. The obtained results indicated that sesuvioside A exhibited inhibitory activity against XO and NO production with the IC50 values of 31.6 µM and 18.3 µM, respectively. At concentration of 40.0 µM, the compound significantly reduced iROS level and the production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 in the lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophages. A molecular docking study revealed that sesuvioside A strongly binds to the targets XO and p-38 MAPK with the estimated energy of -10.55 kcal/mol and -9.78 kcal/mol, respectively. In conclusion, sesuvioside A from the aerial parts of G. celosioides is a new dual anti-gout agent by expressing its inhibitory effects on XO activity and inflammatory targets. The traditional use of G. celosioides as a remedy for gout was supported by the findings in this study.
Resumen. La Gomphrena celosioides Mart. Es muy usada en Vietnam para el tratamiento de la gota (hiperurisemia). A través de un proceso de aislamiento bio-dirigido de inhibidores de la xantina oxidasa (XO), se identificó que el sesuviósido A, el constituyente principal de la fracción butanólica de las partes aéreas de G. celosioides, es un compuesto que mostró actividad farmacológica y es candidato para el desarrollo de medicamentos contra la hiperurisemia. La actividad del sesuviósido A —aislado por primera vez como principal componente de dicha fracción— fue investigada extensamente mediante ensayos biológicos in vitro, incluyendo la inhibición de la actividad de la XO, la producción de óxido nítrico (NO), especies reactivas de oxígeno intracelulares (iROS) y citoquinas proinflamatorias. Los resultados obtenidos indicaron que el sesuviósido A presentó actividad inhibitoria sobre la XO y la producción de NO, con valores de IC₅₀ de 31,6 µM y 18,3 µM, respectivamente. A una concentración de 40,0 µM, el compuesto redujo significativamente los niveles de iROS y la producción de las citoquinas proinflamatorias TNF-α, IL-6 e IL-8 en macrófagos inducidos por lipopolisacáridos. Un estudio de acoplamiento molecular reveló que el sesuviósido A se une fuertemente a los blancos moleculares XO y p38 MAPK, con energías estimadas de -10,55 kcal/mol y -9,78 kcal/mol, respectivamente. En conclusión, el sesuviósido A, aislado de las partes aéreas de G. celosioides, representa un nuevo agente anti-gota dual, al ejercer efectos inhibitorios tanto sobre la actividad de la XO como sobre blancos inflamatorios. Los hallazgos de este estudio respaldan el uso tradicional de G. celosioides como remedio para la gota.
Downloads
References
1. Ragab, G.; Elshahaly, M.; Bardin, T. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 495–511 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2017.04.008.
2. Huddleston, E. M.; Gaffo, A. L. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2022, 65, 102241 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2022.102241.
3. Martinon, F.; Pétrilli, V.; Mayor, A.; Tardivel, A.; Tschopp, J. Nature. 2006, 440, 237–241 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04516.
4. Pouliot, M.; James, M. J.; McColl, S. R.; Naccache, P. H.; Cleland, L. G. Blood. 1998, 91, 1769–1776.
5. So, A.; Thorens, B. J. Clin. Invest. 2010, 120, 1791–1799 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI42344.
6. Panche, A. N.; Diwan, A. D.; Chandra, S. R. J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 5, e47 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/jns.2016.41.
7. Borges, F.; Fernandes, E.; Roleira, F. Curr Med Chem. 2002, 9, 195–217 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867023371229.
8. Mierziak, J.; Kostyn, K.; Kulma, A. Molecules. 2014, 19, 16240–16265 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191016240.
9. Tian, C.; Liu, X.; Chang, Y.; Wang, R.; Lv, T.; Cui, C.; Liu, M. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 137, 257–264 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2020.10.022.
10. Sharma, J. N.; Al-Omran, A.; Parvathy, S. S. Inflammopharmacol. 2007, 15, 252–259 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-007-0013-x.
11. Dejam, A.; Hunter, C. J.; Pelletier, M. M.; Hsu, L. L.; Machado, R. F.; Shiva, S.; Power, G. G.; Kelm, M.; Gladwin, M. T.; Schechter, A. N. Blood. 2005, 106, 734–739 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-02-0567.
12. Larsen, F. J.; Weitzberg, E.; Lundberg, J. O.; Ekblom, B. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 342–347 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.11.006.
13. Shiva, S.; Huang, Z.; Grubina, R.; Sun, J.; Ringwood, L. A.; MacArthur, P. H.; Xu, X.; Murphy, E.; Darley-Usmar, V. M.; Gladwin, M. T. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 654–661 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000260171.52224.6b.
14. Townsend, C. C. Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg. 1993, 70–91 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-02899-5_7.
15. Macorini, L. F. B.; Radai, J. A. S.; Maris, R. S.; Silva-Filho, S. E.; Leitao, M. M.; de Andrade, S. F.; Gelves, D. I. A.; Salvador, M. J.; Arena, A. C.; Kassuya, C. A. L. Evid. Based. Complement. Alternat. Med. 2020, 2020, 4170589 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4170589.
16. Tarnam, Y. A.; Ilyas, M.; Begum, T. N. Int. J. Pharma. Res. Rev. 2014. 3, 58-66.
17. de Paula Vasconcelos, P. C.; Spessotto, D. R.; Marinho, J. V.; Salvador, M. J.; Junior, A. G.; Kassuya, C. A. L. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 202, 85–91 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2017.03.007.
18. Quang, N.; Phuong, N.; Luong, V.; Huyen, N.; Xuan, D.; Thanh, T. Vietnam J.Chem. 2024, 62 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/vjch.202300269.
19. Dosumu, O. O.; Idowu, P. A.; Onocha, P. A.; Ekundayo, O. EXCLI J. 2010, 9, 173–180.
20. Olutola Dosumu, O.; Onocha, P.; Ekundayo, O.; Ali, M. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 143–147.
21. Hoi, H. Pharmacogn. J. 2020, 12, 1693–1697 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5530/pj.2020.12.228.
22. Noro, T.; Oda, Y.; Miyase, T.; Ueno, A.; Fukushima, S. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1983, 31, 3984–3987 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.31.3984.
23. Cheenpracha, S.; Park, E.-J.; Rostama, B.; Pezzuto, J. M.; Chang, L. C. Mar. Drugs. 2010, 8, 429–437 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/md8030429.
24. Han, Y.-H.; Chen, D.-Q.; Jin, M.-H.; Jin, Y.-H.; Li, J.; Shen, G.-N.; Li, W.-L.; Gong, Y.-X.; Mao, Y.-Y.; Xie, D.-P.; et al. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2020, 63, 21 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13765-020-00504-2.
25. Halgren, T. A. J. Comput. Chem. 1999, 20, 720–729 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-987X(199905)20:7<720::AID-JCC7>3.0.CO;2-X.
26. O’Boyle, N. M.; Banck, M.; James, C. A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G. R. J. Cheminf. 2011, 3, 33 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-3-33.
27. Gill, A. L.; Frederickson, M.; Cleasby, A.; Woodhead, S. J.; Carr, M. G.; Woodhead, A. J.; Walker, M. T.; Congreve, M. S.; Devine, L. A.; Tisi, D.; et al. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 414–426 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm049575n.
28. Enroth, C.; Eger, B. T.; Okamoto, K.; Nishino, T.; Nishino, T.; Pai, E. F. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2000, 97, 10723–10728 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.20.10723.
29. Trott, O.; Olson, A. J. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21334.
30. Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A. F.; Forli, S. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3891–3898 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.1c00203.
31. Forli, S.; Huey, R.; Pique, M. E.; Sanner, M. F.; Goodsell, D. S.; Olson, A. J. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 905–919 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2016.051.
32. Disadee, W.; Mahidol, C.; Sahakitpichan, P.; Sitthimonchai, S.; Ruchirawat, S.; Kanchanapoom, T. Tetrahedron. 2011, 67, 4221–4226 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2011.04.041.
33. Zhou, B.; Yang, Z.; Feng, Q.; Liang, X.; Li, J.; Zanin, M.; Jiang, Z.; Zhong, N. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 199, 60–67 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2017.01.038.
34. Ghalib, R. M.; Mehdi, S.; Hashim, R.; Sulaiman, O.; Valkonen, A.; Rissanen, K.; Trifunović, S. J. of Chem. Crystallogr. 2010, 40, 510–513 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10870-010-9687-9.
35. Mahmoud, I. I.; Marzouk, M. S.; Moharram, F. A.; El-Gindi, M. R.; Hassan, A. M. Phytochemistry. 2001, 58, 1239–1244 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-9422(01)00365-x.
36. Xue, H.; Xu, M.; Gong, D.; Zhang, G. Food. Front. 2023, 4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/fft2.287.
37. Li, J.; Gong, Y.; Li, J.; Fan, L. Food. Chem. 2022, 379, 132100 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132100.
38. da Silva, S. L.; da Silva, A.; Honório, K. M.; Marangoni, S.; Toyama, M. H.; da Silva, A. B. F. J. Mol. Struct. THEOCHEM. 2004, 684, 1–7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theochem.2004.04.003.
39. Liang, H.; Deng, P.; Ma, Y.-F.; Wu, Y.; Ma, Z.-H.; Zhang, W.; Wu, J.-D.; Qi, Y.-Z.; Pan, X.-Y.; Huang, F.-S.; et al. Evid. Based. Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 8698232 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8698232.
40. Turner, M. D.; Nedjai, B.; Hurst, T.; Pennington, D. J. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2014, 1843, 2563–2582 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.05.014.
41. Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Li, H. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 23, 1–8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2022.11230.
42. Ying, J.; Zhang, M.; Qiu, X.; Lu, Y. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 381–390 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.088.
43. Yang, L.; He, J. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 55 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-022-03540-1.
44. Huwiler, A.; Wartmann, M.; van den Bosch, H.; Pfeilschifter, J. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 129, 612–618 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0703077.

Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Quang Ngô Văn, Thuy Thanh Thi Thu , Luong Dang Vu, Cuong Trinh Tat , Ha Nguyen Xuan , Cuong Nguyen Manh , Phuong Nguyen Thi Mai

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.









