DFT Study of the Molecular Structure, Conformational Preference, Spectroscopic and Vibrational Analysis of Cinnamic Acid and Cinnamaldehyde
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v66i4.1757Keywords:
Cinnamic acid, cinnamaldehyde, conformational preference, solvent effect, vibrational analysisAbstract
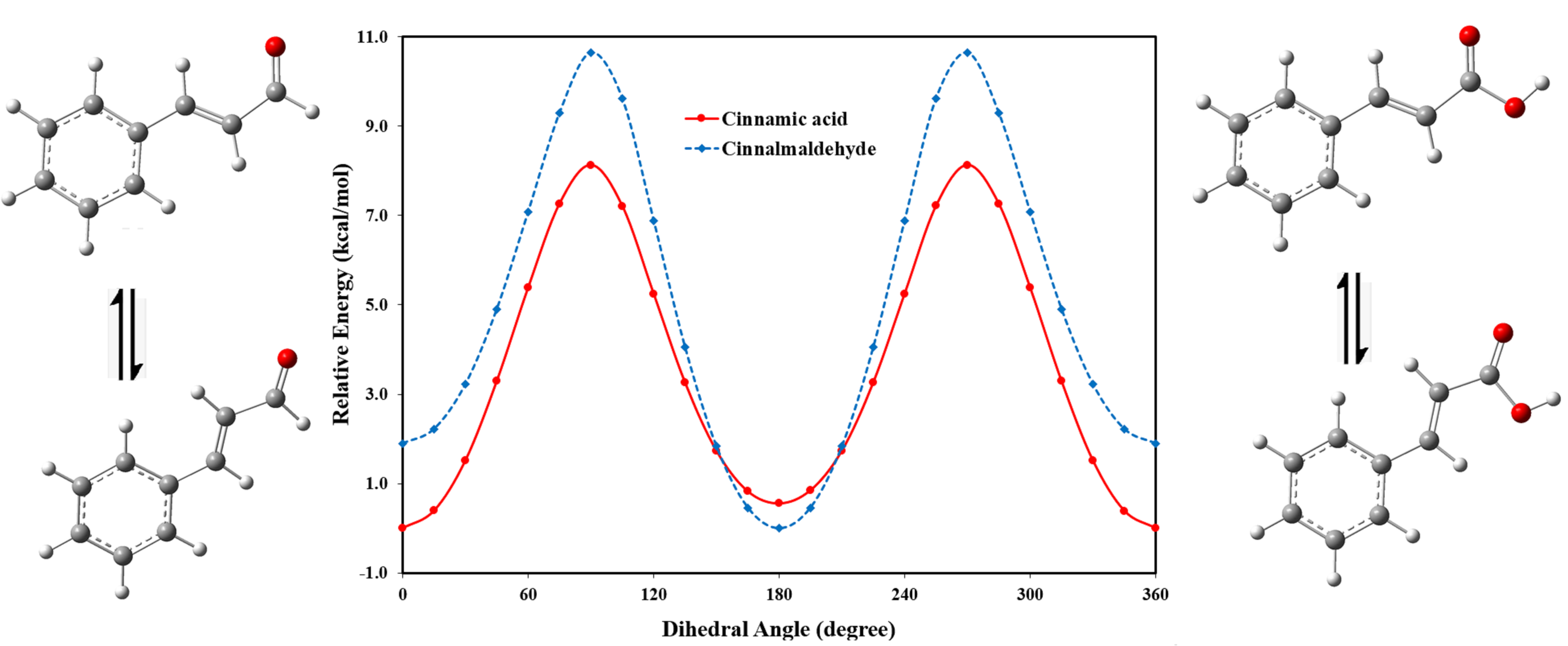
Abstract. B3YLP with the 6-311++G (d, p) basis set was used to investigate the conformational preference, geometrical structure, and spectroscopic properties of the conformational isomers of cinnamic acid and cinnamaldehyde in gas and in solvents. In the gas phase, the s-cis isomer of cinnamic acid was found to be more stable than the s-trans conformer, while for cinnamaldehyde the s-trans conformer was found to be the more stable conformer. The effects of solvents on the conformational preference of these molecules were investigated using the IEF-PCM model. For both cinnamic acid and cinnamaldehyde, the solvent has shown no significant effect on the stability preference. However, the stability of both conformational isomers of cinnamic acid and cinnamaldehyde increases as the dielectric constant of solvent increases, because solvation energies decrease as the dielectric constant of the solvent increases. The 13C and 1H NMR chemical shifts were calculated in DMSO and chloroform. The NBO charges and the UV-visible spectra have been computed in the gas phase, chloroform, methanol, and water.
Resumen. Se utilizó B3YLP con el conjunto de base 6-311++G (d, p) para investigar la preferencia conformacional, la estructura y las propiedades espectroscópicas de los isómeros conformacionales de ácido cinámico y cinamaldehído en fase gas y en solventes. En la fase gaseosa, se encontró que el isómero s-cis del ácido cinámico era más estable que el confórmero s-trans, mientras que para el cinamaldehído se encontró que el confórmero s-trans era el más estable. Los efectos de disolvente sobre la preferencia conformacional de estas moléculas se investigaron utilizando el modelo IEF-PCM. Tanto para el ácido cinámico como para el cinamaldehído, el disolvente no mostró ningún efecto significativo sobre la preferencia de estabilidad. Sin embargo, la estabilidad de ambos isómeros conformacionales de ácido cinámico y cinamaldehído aumenta a medida que aumenta la constante dieléctrica del disolvente, porque las energías de solvatación disminuyen a medida que aumenta la constante dieléctrica del disolvente. Los corrimientos químicos de RMN de 13C y 1H se calcularon en DMSO y cloroformo. Las cargas NBO y los espectros UV-visibles se han calculado en la fase gaseosa, cloroformo, metanol y agua.
Downloads
References
Li, Y.; Kong, D.; Wu, H. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 41, 269–278. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.04.056.
Hoskins, J. A. J. Appl. Toxicol. 1984, 4, 283–292. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.2550040602.
Gende, L., Floris, I., Fritz, R., Eguaras, M. Bulletin of Insectology. 2008, 61, 1-4,
Bickers, D.; Calow, P.; Greim, H.; Hanifin, J. M.; Rogers, A. E.; Saurat, J. H.; Sipes, I. G.; Smith, R. L.; Tagami, H. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 799–836. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2004.09.013.
Liu, L.; Hudgins, W. R.; Shack, S.; Yin, M. Q.; Samid, D. Int. J. Cancer. 1995, 62, 345–350. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.2910620319.
Dhara, L.; Tripathi, A. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-019-03692-y.
Dhara, L.; Tripathi, A. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 65–73. DOI: 10.1007/s12223-020-00806-4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-019-03692-y
Tripathy, M. IJPSR. 2017, 8, 2333–2340. DOI: https://doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.8(6).2333-40.
Hoi, J. K.; Lieder, B.; Pignitter, M.; Hans, J.; Ley, P.; Lietard, J.; Hölz, K.; Somoza, M. M.; Somoza, V. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 11638–11649. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b04274.
Joint, F. A. O.; Additives, W. H. O. E. C. on F.; Organization, W. H. Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants: Fifty-Fifth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; World Health Organization, 2001.
Burdock, G. A. Fenaroli’s, In: Flavor Ingredients: Vol. 2; CRC press, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1201/9780429292897
Lamb, C. J.; Rubery, P. H. Anal. Biochem. 1975, 68, 554–561. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(75)90651-X.
Hsieh, T.-J.; Su, C.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Liou, C.-H.; Lu, L.-H. J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 741, 193–199. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2005.02.009.
Kalinowska, M.; Świsłocka, R.; Lewandowski, W. J. Mol. Struct. 2007, 834–836, 572–580. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2006.11.043.
Vinod, K. S.; Periandy, S.; Govindarajan, M. Spectrochim. Acta Part A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.09.098.
Sirichote, O.; Hansongnern, K.; Yaochuang, Y.; Jantaraprim, C. J. Sci. Soc. Thailand. 1996, 333–342. DOI: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.1996.22.333. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.1996.22.333
Al-bayati, F. A.; Mohammed, M. J.; Al-bayati, F. A.; Mohammed, M. J. Pharm. Biol. 2009, 0209. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/13880200802430607.
Al-Bayati, F. A.; Mohammed, M. J. Pharm. Biol. 2009, 47, 61–66. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/13880200802430607.
Hoi, J. K.; Lieder, B.; Pignitter, M.; Hans, J.; Ley, J. P.; Lietard, J.; Hoelz, K.; Somoza, M.; Somoza, V. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 11638–11649. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b04274. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b04274
Vinod, K. S.; Periandy, S.; Govindarajan, M. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 136, 808–817. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.09.098.
Liang, Q.; Chai, K.; Lu, K.; Xu, Z.; Li, G.; Tong, Z.; Ji, H. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 43502–43511. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra07813g.
Yu, C.; Li, Y.-L.; Liang, M.; Dai, S.-Y.; Ma, L.; Li, W.-G.; Lai, F.; Liu, X.-M. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 19124–19133. DOI: DOI: 10.1039/c9ra10820c. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA10820C
Umar, Y.; Abdalla, S. J. Solution Chem. 2017, 46, 741–758. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-017-0601-3.
Umar, Y.; Tijani, J.; Abdalla, S. J. Struct. Chem. 2016, 57, 1545–1553. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022476616080084.
Umar, Y.; Tijani, J. J. Struct. Chem. 2015, 56, 1305–1312. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022476615070112.
Gaussian 09, R. A. 1, Frisch, M. J.; Trucks, G. W.; Schlegel, H. B.; Scuseria, G. E.; Robb, M. A.; Cheeseman, J. R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G. A. et al., Gaussian. Inc., Wallingford CT, 2009.
Becke, A. D. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.464913.
Lee, C.; Yang, W.; Parr, R. G. Phys. Rev. B. 1988, 37, 785. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.37.785.
Sousa, S. F.; Fernandes, P. A.; Ramos, M. J. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2007, 111, 10439–10452. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0734474.
Dennington, R.; Keith, T. A.; Millam, J. M. GaussView, 2016, Version 6.0. 16. Semichem Inc Shawnee Mission KS.
Umar, Y. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1264, 133230. DOI: https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.133230.
Tomasi, J.; Persico, M. Chem. Rev. 1994, 94, 2027–2094. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00031a013.
Tomasi, J.; Mennucci, B.; Cammi, R. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 2999–3094. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/cr9904009.
Cances, E.; Mennucci, B.; Tomasi, J. J. Chem. Phys. 1997, 107, 3032–3041. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.474659.
Mennucci, B.; Cances, E.; Tomasi, J. J. Phys. Chem. B. 1997, 101, 10506–10517. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp971959k.
Miertuš, S.; Scrocco, E.; Tomasi, J. Chem. Phys. 1981, 55, 117–129. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-0104(81)85090-2.
Cammi, R.; Tomasi, J. J. Comput. Chem. 1995, 16, 1449–1458. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.540161202.
Cancès, E.; Mennucci, B. J. Math. Chem. 1998, 23, 309–326. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019133611148.
Jamroz, M. H. Vibrational Energy Distribution Analysis VEDA 4, Warsaw Poland, 2004.
Jamróz, M. H. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 114, 220–230. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2013.05.096.
Alagona, G.; Ghio, C.; Nagy, P. I. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2004, 99, 161–178. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/qua.20117.
http://sdbs.db.aist.go.jp (National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology), accessed on 14th July 2015.
Socrates, G. Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies, Engl. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 2001.
Booth, H.; Silverstein, R.M.; Bassler, G. C.; Morrill, T. C. Magn. Reson. Chem. 1992, 30, 364. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/mrc.1260300417.
Kalsi, P. S., in: Spectroscopy of Organic Compounds 6th Edition. New Dalhi, India New age Int. Publ. 2004.
Umar, Y.; Abdalla, S.; Haque, S. K. M.; Moran, G. S.; Ishaq, A.; Villada, W. C.; Leone, J. D.; Bunster, M. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2020, 67, 62–71. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jccs.201900051.
Umar, Y. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1–12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05791-5.
Abdalla, S.; Springborg, M. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2011, 978, 143–151. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comptc.2011.10.007.
Umar, Y.; Parlak, C.; Haque, S. K. M.; Appu, S. P.; Ashwaq, O.; Ramasami, P. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2021, 98, 100032. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jics.2021.100032.
Abdalla, S.; Umar, Y.; Mokhtar, I. Z. Phys. Chem. 2016, 230. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/zpch-2015-0700.
Abdalla, S.; Springborg, M. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2010, 114, 5823–5829. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9102096.
Umar, Y. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 2015, 8, 44–55.

Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Fatima Fadl, Sahar Abdalla, Abdurrahman Ishaq, Yunusa Umar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.









