Antimicrobial Effect on Pathogenic Microorganisms and Physicochemical Characterization of Zn-MgO Nanocomposites
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v70i1.2475Keywords:
ZnO-MgO Nanocomposites, microwave synthesis, antimicrobial activityAbstract
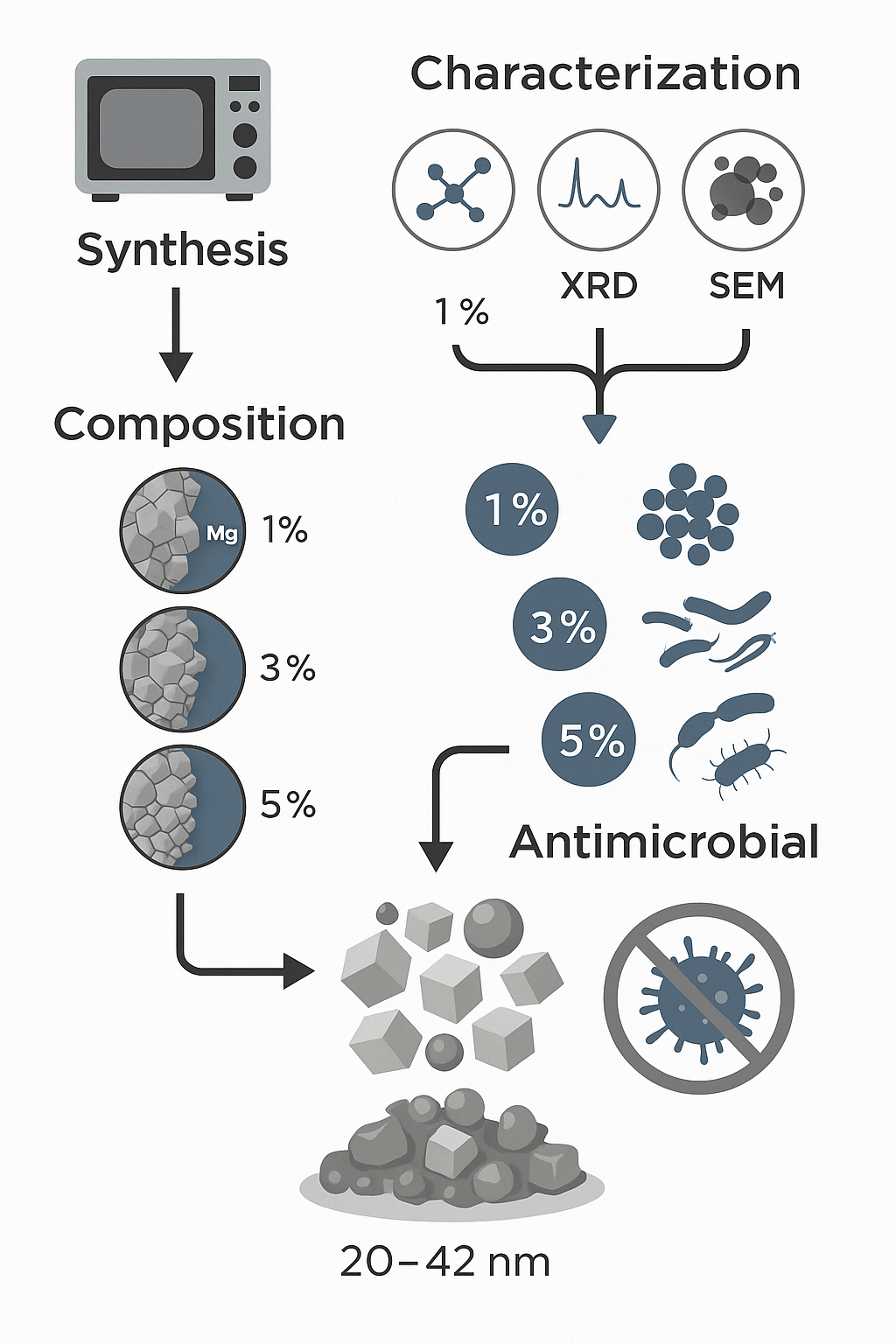
Abstract. Zn-MgO nanocomposites have attracted interest due to their antimicrobial potential against pathogens. The antimicrobial activity of ZnO/MgO mixed oxides with different ratios (1 %, 3 %, 5 % w/w) was evaluated against Escherichia coli, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella paratyphi A, and Listeria monocytogenes. The nanomaterials were synthesized using the microwave method and characterized by FT-IR, XRD, and SEM, confirming the presence of Zn-O and Mg-O bonds, particle sizes ranging from 20 to 42 nm, and cubic/semiglobular morphologies. The results revealed that the addition of MgO influences the particle size and the MgO ratio used, with 1 % ZM being the most effective treatment. This study contributes to the development of new antimicrobial agents to combat the growing bacterial resistance.
Resumen. Los nanocompuestos de Zn-MgO han despertado interés por su potencial antimicrobiano contra patógenos. Se evaluó la actividad antimicrobiana de óxidos mixtos de ZnO/MgO con diferentes relaciones (1 %, 3 %, 5 % w/w) sobre Escherichia coli, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella paratyphi A y Listeria monocytogenes. Los nanomateriales fueron sintetizados mediante el método de microondas y caracterizados por FT-IR, DRX y SEM, confirmando la presencia de enlaces Zn-O y Mg-O, tamaños de partícula entre 20-42 nm y morfologías cúbicas/semiglobulares. Los resultados revelaron que la adición de MgO influye en el tamaño de partícula y la relación de MgO utilizada, siendo el mejor tratamiento ZM 1 %. Este estudio contribuye al desarrollo de nuevos agentes antimicrobianos para combatir la creciente resistencia bacteriana.
Downloads
References
1. Fadl, F. I. A.; Hegazy, D. E.; Maziad, N. A.; Ghobashy, M. M. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 250, 126248.
2. Gnanam, S.; Shynu, R. K.; Gajendiran, J.; Karthikeyan, M.; Ramana Ramya, J.; Thennarasu, G. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2024, 857, 141702.
3. Nigam, A.; Saini, S.; Rai, A. K.; Pawar, S. J. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 19515–19525.
4. Halfadji, A.; Bennabi, L.; Giannakis, S.; Marrani, A. G.; Bellucci, S. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 39097–39108.
5. Elbasuney, S.; El-Sayyad, G. S.; Tantawy, H.; Hashem, A. H. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 25961–25975.
6. Jin, S. E.; Jin, H. E. Nanomaterials. 2021, 11, 263.
7. Kumar, P.; Saravanan, P.; Baskar, G.; Chitrashalini, S.; Omer, S. N.; Subashini, S.; et al. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 170, 113443.
8. Garza-Cervantes, J. A.; Escárcega-González, C. E.; Díaz Barriga Castro, E.; Mendiola-Garza, G.; Marichal-Cancino, B. A.; López-Vázquez, M. A.; et al. Int. J. Nanomedicine. 2019, 14, 2557–2571.
9. EL-Moslamy, S. H. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3820.
10. Yang, X.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Q.; Nie, F.; Du, H.; Pang, X.; et al. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 240.
11. Bondarenko, O.; Juganson, K.; Ivask, A.; Kasemets, K.; Mortimer, M.; Kahru, A. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1181–1200.
12. Champagne, C.P.; Ross, R. P.; Saarela, M.; Hansen, K. F.; Charalampopoulos, D. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 149, 185–193.
13. Christobel, G. J. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2013, 5, No. NOV164755.
14. CH, A.; Rao, K. V.; Chakra, CH. S. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 06.
15. Kayani, Z. N.; Iqbal, M.; Riaz, S.; Zia, R.; Naseem, S. Mater. Sci.-Pol. 2015, 33, 515–520.
16. Rouchdi, M.; Salmani, E.; Fares, B.; Hassanain, N.; Mzerd, A. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 620–627.
17. Yousefi, R.; Zak, A. K.; Jamali-Sheini, F. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2013, 16*, 771–777.
18. Dobrucka, R. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 101, 2046–2057.
19. Kumar, A.; Pandey, A. K.; Shanker, R.; Dhawan, A. Microorganisms 2012.
20. Al-Bedairy, M.; Alshamsi, H. A. H. Eurasian J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 13, No. 6.
21. Shi, X. H.; Ban, J. J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Z. P.; Jia, D. Z.; Xu, G. C. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 16189–16195.
22. Zaidi, B.; Belghit, S.; Ullah, M. S.; Hadjoudja, B.; Guerraoui, A.; Gagui, S.; et al. Metallofiz. Noveishie Tekhnol. 2019, 41, 1121–1126.
23. Kumar, R.; Sharma, A.; Kishore, N. Int. J. Eng. Appl. Manag. Sci. Paradigms 2013, 07.
24. Sankara Reddy, B.; Venkatramana Reddy, S.; Koteeswara Reddy, N. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 2013, 24, 5204–5210.
25. Auger, S.; Henry, C.; Péchaux, C.; Lejal, N.; Zanet, V.; Nikolic, M. V.; et al. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109421.
26. Guan, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J.; Wu, H.; Li, W.; Sun, Q. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123542.

Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Miramontes Escobar Herenia Adilene, Ruvalcaba-Díaz Betsy Krisel, Sánchez Burgos Jorge Alberto, Suresh Ghotekar, Mamoun Fellah, Pérez-Larios Alejandro

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.