A Study of the Structural Features and Textural Properties of Carbon Sorbents Derived from Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate and Polyethylene Waste
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v70i1.2438Keywords:
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyethylene (PE), carbon sorbent, porous structureAbstract
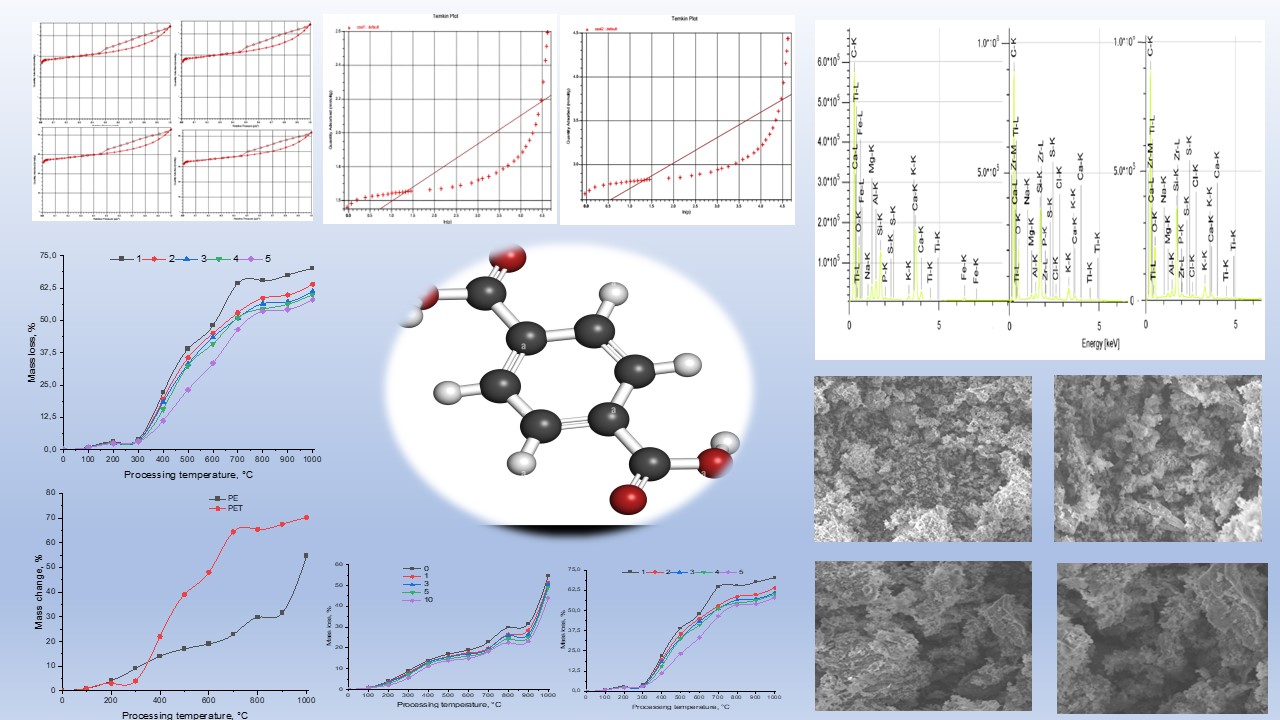
Abstract. This article presents the results of a study on carbon sorbents obtained from recycled polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polyethylene (PE) waste. The research focused on analyzing the structural features and textural properties of the sorbents, as well as their adsorption capabilities. It was found that the specific surface area of sorbents derived from PET with the addition of oxidized graphite reached 318.76 m²/g, while similar materials based on PE achieved up to 420.47 m²/g. These parameters, combined with an increased volume of micropores and mesopores, significantly enhance adsorption efficiency, particularly in water purification applications.
The addition of a pore-forming resulted in a further increase in specific surface area, reaching 825.99 m²/g for PET-OG10 and 1011.78 m²/g for PE-OG10, making these materials particularly promising for adsorption processes. Experimental results confirmed that such carbon-based sorbents effectively remove heavy metals and organic pollutants from water due to their well-developed micro- and mesoporous structure. Thus, the findings of this study
highlight the potential of recycled polymeric materials for the development of novel high-performance sorbents, contributing to enhanced environmental safety and sustainable waste management.
Resumen. Este artículo presenta los resultados de un estudio sobre sorbentes de carbono obtenidos a partir de residuos reciclados de politereftalato de etileno (PET) y polietileno (PE). La investigación se centró en el análisis de las características estructurales y las propiedades texturales de los sorbentes, así como en su capacidad de adsorción. Se encontró que el área superficial específica de los sorbentes derivados del PET con la adición de grafito oxidado alcanzó los 318.76 m²/g, mientras que materiales similares basados en PE lograron hasta 420,47 m²/g. Estos parámetros, combinados con un aumento en el volumen de microporos y mesoporos, mejoran significativamente la eficiencia de adsorción, particularmente en aplicaciones de purificación de agua.
La adición de un porógeno resultó en un aumento adicional del área superficial específica, alcanzando 825.99 m²/g para PET-OG10 y 1011.78 m²/g para PE-OG10, lo que hace que estos materiales sean especialmente prometedores para los procesos de adsorción. Los resultados experimentales confirmaron que estos sorbentes a base de carbono eliminan eficazmente metales pesados y contaminantes orgánicos del agua, gracias a su estructura bien desarrollada de micro y mesoporos. Por lo tanto, los hallazgos de este estudio destacan el potencial de los materiales poliméricos reciclados para el desarrollo de nuevos sorbentes de alto rendimiento, contribuyendo así a una mayor seguridad ambiental y a una gestión sostenible de residuos.
Downloads
References
1. Rhodes, C.J. Sci. Prog. 2018, 101, 207–260. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3184/003685018X15294876706211
2. Hammer, J.; Kraak, M.H.; Parsons, J.R. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 220, 1–44. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-3414-6_1
3. Landrigan, P.J.; Raps, H.; Cropper, M.; Bald, C.; Brunner, M.; Canonizado, E.M.; … Dunlop, S. Ann. Glob. Health 2023, 89, 23. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5334/aogh.4331
4. Williams, A.T.; Rangel-Buitrago, N. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 176, 113429. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.113429
5. Afshar, S.V.; Boldrin, A.; Astrup, T.F.; Daugaard, A.E.; Hartmann, N.B. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140000.
6. Dey, S.; Veerendra, G.T.N.; Anjaneya Babu, P.S.S.; Phani Manoj, A.V.; Nagarjuna, K. Biomater. Devices. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44174-023-00085-w
7. Alaghemandi, M. Sustainability. 2024, 16, 10401. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su162310401
8. Kumar, R.; Verma, A.; Shome, A.; Sinha, R.; Sinha, S.; Jha, P.K.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, P.; Shubham; Das, S.; et al. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9963. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179963
9. Cubas, A.L.V.; Moecke, E.H.S.; Provin, A.P.; Dutra, A.R.A.; Machado, M.M.; Gouveia, I.C. Polymers (Basel). 2023, 15, 3151. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153151
10. Tumu, K.; Vorst, K.; Curtzwiler, G. J. Environ. Manage. 2023, 348, 119242. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.119242
11. Tsuchimoto, I.; Kajikawa, Y. Sustainability. 2022, 14, 16340. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416340
12. Dokl, M.; Copot, A.; Krajnc, D.; Fan, Y.V.; Vujanović, A.; Aviso, K.B.; Tan, R.R.; Kravanja, Z.; Čuček, L. Sustainable Production and Consumption. 2024, 51, 498–518. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2024.09.025
13. Joseph, T.M.; Azat, S.; Ahmadi, Z.; Jazani, O.M.; Esmaeili, A.; Kianfar, E.; Haponiuk, J.; Thomas, S. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 9, 100673. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscee.2024.100673
14. Massoud, T.; Dsilva, J. Next Sustainability. 2025, 6, 100095. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nxsust.2024.100095
15. Dayal, L.; Yadav, K.; Dey, U.; Das, K.; Kumari, P.; Raj, D.; Mandal, R.R. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 16, 100460. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hazadv.2024.100460
16. Mendoza-Carrasco, R.; Cuerda-Correa, E.M.; Alexandre-Franco, M.F.; Fernández-González, C.; Gómez-Serrano, V. J. Environ. Manage. 2016, 181, 522–535. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.06.070
17. Almazán-Almazán, M.C.; Pérez-Mendoza, M.; Domingo-García, M.; Fernández-Morales, I.; López, F.J.; López-Garzón, F.J. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 236–242. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2009.10.003
18. Rai, P.; Singh, K. P. J. Environ. Manage. 2018, 207, 249–261. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.11.047
19. Khoshimov, S.; Raxmonaliyeva, N.; Askarova, D.; Seytnazarova, O.; Abdikamalova, A. AIP Conf. Proc. 2024, 3045, 030059. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0197789
20. Alhulaybi, Z.; Dubdub, I. Polymers, 2023, 15. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15143010
21. Turnbull, L., Liggat, J. J., & Macdonald, W. A. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 2244–2258. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2013.08.018
22. EP0273274B1. Degradation of polyethylene by means of agents generating free radicals. Applicant: Elf Atochem Deutschland GmbH (DE). Publication date: 12 July 2000. Bulletin 2000/28. Application No. 87118394.3, filed 11 Dec 1987, priority date: 11 Dec 1986 (DE3642266). Available at: https://patents.google.com/patent/EP0273274B1/en
23. Chia, J.W.F.; Sawai, O.; Nunoura, T. Waste Manag. 2020, 108, 62–69. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.04.035
24. Chen, S.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, S.; Hou, H. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136250. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136250
25. Dimitrov, N.; Kratofil Krehula, L.; Ptiček Siročić, A.; Hrnjak-Murgić, Z. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 972–979. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2013.02.013
26. Zheng, G.; Wu, J.; Wang, W.; Pan, C. Carbon. 2004, 42, 2839–2847. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2004.06.029
27. Xu, X. B.; et al. Carbon. 2005, 43, 1479–1487.
28. Bayburdov, T. A.; Shipovskaya, A. B. Izv. Saratov Univ. New Ser. Chem. Biol. Ecol. 2018, 18, 285–298. DOI: https://doi.org/10.18500/1816-9775-2018-18-3-285-298
29. Smolii, V. A.; Kosarev, A. S.; Yatsenko, E. A. Glass Ceram. 2020, 77, 94–97. DOI: https://doi.org/10.59957/jctm.v60.i1.2025.510.1007/s10717-020-00247-y
30. Seitnazarova, O.; Kalbaev, A.; Mamataliev, N.; Abdikamalova, A.; Najimova, N. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2025, 60. DOI: https://doi.org/10.59957/jctm.v60.i1.2025.5
31. Mamataliev, N.; Abdikamalova, A.; Eshmetov, I.; Kalbaev, A. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2023, 58. DOI: https://doi.org/10.59957/jctm.v58i6.140
32. Erdogan, F. Freundlich, Langmuir, Temkin, DR and Harkins-Jura. Int. J. Chem. Reactor Eng. 2019, 17, 20180134. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/ijcre-2018-0134
33. Yu, A.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, H. Water. 2021, 13, 608. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/w13050608

Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Alisher Kalbaev, Aziza Abdikamalova, Dilzoda Asqarova, Shahrom Khoshimov, Rahimjon Paygamov , Khayot Bakhronov , Kamoliddin Kholikov , Dilnoza Salikhanova , Dilnoza Jumaeva, Izzat Eshmetov, Nursultan Maratov, Mamataliev Nozim

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.