Alkanes and Chemical Markers Identified in the Essential Oil from Pericarp of Nanfengmiju (Citrus kinokuni Hort. ex Tanaka)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v67i1.1819Keywords:
Alkanes, chemical markers, tricosane, essential oils, Nanfengmiju (Citrus kinokuni Hort. ex Tanaka)Abstract
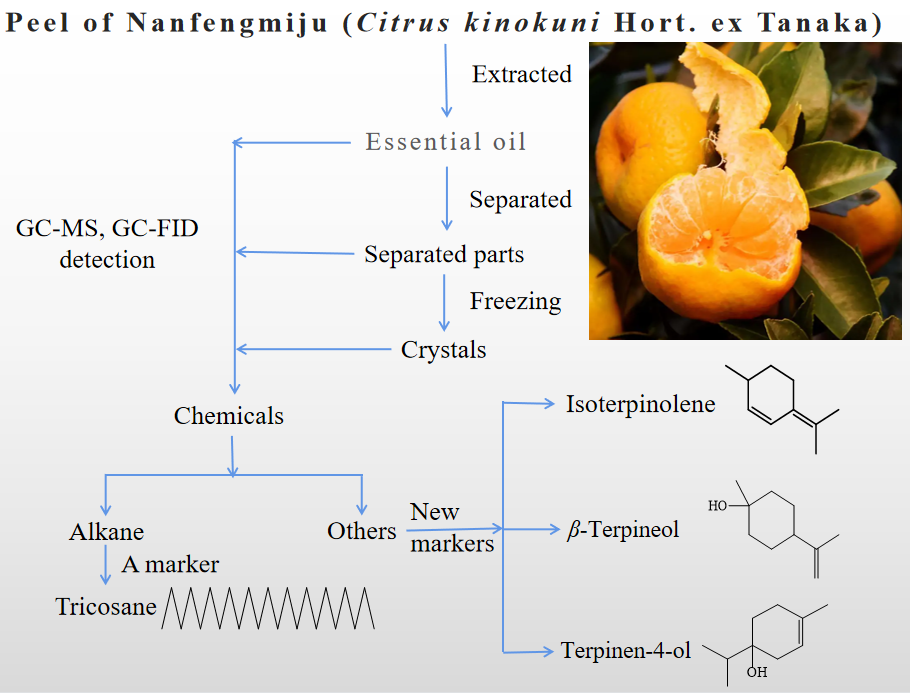
Based on the previously researches, this manuscript comprehensively analysed the chemicals in essential oil (EO) from pericarp of Nanfengmiju, a variety of Citrus kinokuni Hort. ex Tanaka. The isolated crystals from the EO were mainly composed of a series of alkanes. In total, 33 alkanes were identified, in which 14 ones were firstly reported in the peels EOs from Citrus L., to the best of my knowledge. Previously, alkanes were neglected and never thought as the chemical markers of peels EOs from Citrus. In fact, some of them can be chosen as the markers such as tricosane and pentacasane. Eight compounds including limonene, γ-terpinene, α-terpineol, α-farnesene, linalool, thymol, α-sinensal, and methyl-N-methyl anthranilate had already been identified as the markers of peels EOs from Citrus reticulata Blanco. α-Sinensal and methyl-N-methyl anthranilate were undetected in this study. At the same time, another 2 compounds β-terpineol and δ-cadinene were first selected, and 2 compounds such as spathulenol and isospathulenol were identified previously as the markers of peel EO from Nanfengmiju. In total, twelve markers were identified for peels EO from Nanfengmiju.
Resumen. Con base en investigaciones previas, en este trabajo se analizan exhaustivamente los productos químicos presentes en el aceite esencial (EO) del pericarpio de Nanfengmiju, una variedad de Citrus kinokuni Hort. ex Tanaka. Los cristales aislados del EO estaban compuestos principalmente por una serie de alcanos. En total, se identificaron 33, entre los cuales, de acuerdo con lo que sabemos, 14 se informaron por primera vez en los aceites esenciales de cáscaras de Citrus L. En este trabajo se proponen algunos alcanos como marcadores químicos de los aceites esenciales de las cáscaras de cítricos, como el tricosano y el pentacasano. Ocho compuestos, incluidos limoneno, γ-terpineno, α-terpineol, α-farneseno, linalol, timol, α-sinensal y antranilato de metil-N-metilo, ya se han identificado como marcadores de AE de cáscaras de Citrus reticulata Blanco. En este estudio no se detectaron ni el α-sinensal ni el antranilato de metil-N-metilo. Al mismo tiempo, se seleccionaron otros 2 nuevos marcadores: β-terpineol y δ-cadineno, y compuestos como el espatulenol y el isospatulenol se identificaron previamente como marcadores del EO de la cáscara de Nanfengmiju. En total, se identificaron doce marcadores para EO de Nanfengmiju.
Downloads
References
Huang, C.C., In: Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae Tomus, 43(2). 1st Ed., Delectis Florae Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae Agendae Academiae Sinicae Edita, Science Press, Beijing, China, 1997, 175-210. (Book in Chinese).
Pharmacopoeia committee of the People’s Republic of China. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, Vol. 1, 1st Ed, China Medical Science and Technology Press, Beijing, China, 2020, 199-200, 205-206. (Book in Chinese).
González-Mas, M.C.; Rambla, J.L.; López-Gresa, M.P.; Blázquez, M.A.; Granell, A. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00012
Cannon, R.J.; Kazimierski, A.; Curto, N.L.; Li, J.; Trinnaman, L.; Jańczuk, A.J.; et al. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 1915-1931. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jf505177r
Baik, J.S.; Kim, S.S.; Lee, J.A.; Oh, T.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, N.H.; Hyun, C.G. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 18, 74–79.
Dugo, P.; Mondello, L., in: Medicinal and Aromatic Plants - Industrial Profiles, Vol. 49, Hardman, R., Ed., CRC Press, Florida, American, 2011, 30.
Pashazanousi, M.B.; Raeesi, M.; Shirali, S. Asian J. Chem. 2012, 24, 4331-4334.
Yu, L.F.; Li, X.R.; Liu, S.Y.; Xu, G.W.; Liang, Y.Z. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 3457–3465. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200900267
Choi, H.S. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3254–3258. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jf052409j
Zhang H.P., Xie Y.X., Liu C.H., Chen S.L., Hu S.S., Xie Z.Z., Deng X.X., Xu J. Food Chem. 2017, 230, 316–326 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.03.040
Verzera, A.; Trozzi, A.; Gazea, F.; Cicciarello, G.; Cotroneo, A. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 206-210. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0206872
Blázquez, M.A.; Carbó, E. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 76, 515-521. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.07.019
Minh Tu, N.T.; Thanh, L.X.; Une, A.; Ukeda, H.; Sawamura, M. Flavour Frag. J. 2002, 17, 169–174. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ffj.1076
Sawamura, M.; Minh Tu, N.T.; Yu, X.L.; Xu, B.Q. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2005, 17, 2-6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10412905.2005.9698813
Lan-Phi, N.T.; Shimamura, T.; Ukeda, H.; Sawamura, M. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 1042-1047. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.12.024
Flamini, G.; Cioni, P.L. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 984-992. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.11.037
Pan Z.; Han T.L.; Wang J. Acta Sci. Agric. 2018, 2, 167-178.
Khan, M.M.; Iqbal, M.; Hanif, M.A.; Mahmood, M.S.; Naqvi, S.A.; Shahid, M.; et al. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Pl. 2012, 15, 972-979. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/0972060X.2012.10662601
Wang, J.; Liu, Y.P.; Chen, H.P.; Chen, L.; Wei, Z.; Liu, R.; Fei, L.; Wan, D. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 6434-6442.
Han, T.L.; Ullah, I.; Wang, J. Acta Sci. Agric. 2020, 4, 4-26.
Benelli, P.; Riehl, C.A.S.; Smânia, A.; Smânia, E.F.A.; Ferreira, S.R.S. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2010, 55, 132-141. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2010.08.015
Bosco, S.F.D.; Abbate, L.; Mercati, F.; Napoli, E.; Ruberto, G., in: The Citrus Genome, Gentile, A.; Malfa, S.L.; Deng, Z., Ed., Springer Nature Switzerland AG, Switzerland, 2020, 211-224.
Lota, M.L.; Serra, D.R.; Tomi, F.; Casanova, J. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2001, 29, 77-104. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0305-1978(00)00029-6
Shiota, H.; Itoo, S. Flavour Frag. J. 1991, 6, 57-62. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ffj.2730060107
Duan, L.; Guo, L.; Dou, L.L.; Zhou, C.L.; Xu, F.G.; Zheng, G.D.; et al. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 123–127. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.05.141
Tao, N.; Jia, L.; Zhou, H. Food Chem. 2014, 153, 265-271. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.12.070
Fanciullino, A.L.; Tomi, F.; Luro, F.; Desjobert J.M.; Casanova, J. Flavour Fragr. J. 2006, 21, 359-367. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ffj.1658
Bourgou, S.; Rahali, F.Z.; Ourghemmi, I.; Tounsi, M.S. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 528593. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1100/2012/528593
Pino, J.A.; Muñoz, Y.; Quijano-Celís, C.E. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Pl. 2006, 3, 271-276. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/0972060X.2006.10643503
Espina, L.; Somolinos, M.; Lorán, S.; Conchello, P.; García, D.; Pagán, R. Food Control, 2011, 22, 896-902. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2010.11.021
Dong, Z.B.; Shao, W.Y.; Liang, Y.R. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 4975-4978. DOI: https://doi.org/10.14233/ajchem.2014.16277
Zakaria, Z.; Zakaria, S.; Mohd Ishak, M.A. Sains Malaysiana. 2010, 39, 565-569.
Wang, J. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2018, 10, 133-137.
Gross, J.H. Mass spectrometry. Science Press, Beijing, China, 2015. 299.

Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Jian Wang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.









